Lipids
100 likes | 331 Vues
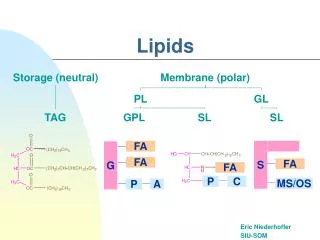
Lipids. Macromolecule #2: Lipids. Hydrophobic (nonpolar) = insoluble in water Contain C, H, O (less O than carbs), sometimes P Main types: Triglycerides (fats & oils) Phospholipids Steroids. 1. Triglycerides (fats & oils). Saturated = each C has 4 single covalent bonds with H

Lipids
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Macromolecule #2: Lipids • Hydrophobic (nonpolar) = insoluble in water • Contain C, H, O (less O than carbs), sometimes P Main types: • Triglycerides (fats & oils) • Phospholipids • Steroids
1. Triglycerides (fats & oils) Saturated = each C has 4 single covalent bonds with H Unsaturated= presence of one or more double bonds Contain glycerol + three fatty acids FUNCTIONS: Energy storage, cushioning, insulation
The bad saturated fat Found in fats of mostly animal origin • Large amounts of saturated fat increase the risk of heart disease • ↑ both LDL (“bad” lipoprotein) & HDL (“good” lipoprotein) • LDL may deposit cholesterol on arteries; HDL carries cholesterol from blood to liver where it may be stored
Found inolive oil, canola oil, peanut oil, fish oil, nuts ↓ LDL (bad lipoprotein) Unsaturated oils = the good lipids
Hydrogenated fats = the worst guys Also called trans fats;hydrogens are added synthetically to unsaturated oils to make them solids at room T margarine, crisco ↑ LDL and ↓ HDL
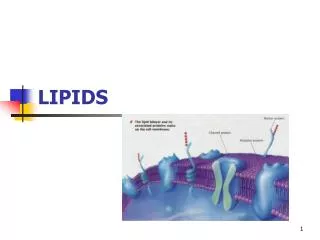
2. Phospholipids Found in cell membranes
3. Steroids Functions of cholesterol: • Increases stability of all animal cell membranes • Needed to make bile (bile is needed for digestion of fats) • Precursor to steroid hormones, e.g. testosterone, estrogen, calcitriol
4. Other Lipids Eicosanoids– “local hormones”; LOTS of functions: • Contribute to inflammatory and immune response • Control other hormones • Prevent stomach ulcers • Regulate body T • Influence formation of blood clots Derived from omega-3 and omega-6 essential fatty acids