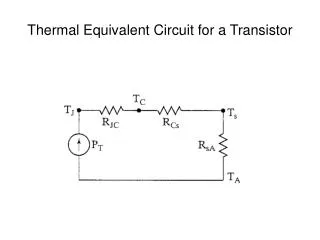
RTD (Resistance temperature detector)
1.35k likes | 5.24k Vues
RTD (Resistance temperature detector). Varying resistance with temperature Good for measurement of small temperature differences General equation for RTD material Rt = Ro(1+ At + Bt 2 + Ct 3 - - - - - Wt 4 ) B,C - - -W are negligibly small. Rt = Ro(1+ At).

RTD (Resistance temperature detector)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
RTD (Resistance temperature detector) • Varying resistance with temperature • Good for measurement of small temperature differences • General equation for RTD material Rt = Ro(1+ At + Bt2 + Ct3 - - - - - Wt4 ) B,C - - -W are negligibly small. Rt = Ro(1+ At)
RTDs: Characteristics and Applications • Characteristics: • Resistive device, linear • Large range: -200 to +850oC for Platinum • High accuracy: 0.001oC • Low sensitivity: 0.39 % per oC • Don’t need reference temperature • Applications: • Industries and laboratories where high accuracy of temperature measurements are required.
Requirements for RTD material • High temperature coefficient • High resistivity to ensure small wire length • Linearity of relation between resistance and temperature • Sufficient mechanical strength • Stability of electrical characteristics
Construction • A thin Platinum wire wound in form of a free spiral by an insulated carrier such as mica or ceramic. • Diameter of wire should be 0.02mm to 0.2mm. • Wire should be smooth, free from defects, ensurity of constancy of resistance to avoid resistance changes due to dimension changes. • Wire generally enclosed in a protective tube made of glass, quartz etc.
Calendar-Van Dusen Equation For platinum, the resistance temperature relationship is given by the following equation: (U.S. calibration curve For the U. S. calibration curve, a = 0.003851/°C
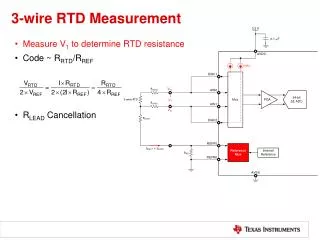
R1 R2 Vo Vs R4 RRTD RTD’s small resistance change requires • Bridge circuit: • Can detect small resistance changes “Supply” Voltage
RTD Materials Gold & Silver: Rarely used because of low resistivity Tungsten: Very high resistivity Gold Silver alloy: Give same characs As Platinum below 1250 C. Phosphor Bronze alloy: Better for low temperature measurement Nickel: Most used, cheaper than platinum Platinum: More suitable but expensive, high range, high precision
RTD Advantages • Very accurate • Very stable • Standardized among vendors • Large variety of packaging options
RTD Disadvantages • Costly • Require current source or voltage source • Low resistance/small change • 4-wire measurement • Slow