Understanding and Measuring Angles: A Complete Guide
150 likes | 280 Vues
This guide explains the concepts of naming and measuring angles, starting from basic definitions to practical measurement techniques using a protractor. When two lines meet at a point, they form an angle at the vertex. For example, angles can be named as ∠MON or ∠NOM. Angles are measured in degrees, with examples demonstrating various angles such as 30°, 60°, and 120°. A step-by-step process is provided on how to use a protractor effectively, ensuring accurate angle measurement in different scenarios.

Understanding and Measuring Angles: A Complete Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Naming and Measuring Angles • Understanding angles • Measuring angles
Naming and Measuring Angles angle When two lines meet at a point, an angle is formed.
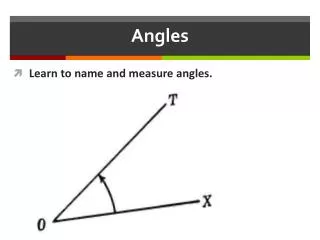
Naming and Measuring Angles M N Line MO and line NO meet at the point O. O Point Ois called the vertex.
Naming and Measuring Angles M N We refer to the angle formed at vertex O as ∠MON or ∠NOM. O
Naming and Measuring Angles M We can also label the angle as p and name it ∠p. N p We refer to the angle formed at vertex O as ∠MON or ∠NOM. O
Naming and Measuring Angles Read the following angles: T ∠UTS M ∠w N w U p P S O ∠NOM ∠p e Q ∠PQR R ∠e
Naming and Measuring Angles Angles are measured in degrees and are written with the ‘°’ symbol; such as 90°. To measure an angle in degrees, I can use a protractor.
Naming and Measuring Angles Slide protractor along one of the line.
Naming and Measuring Angles Place the centre of the base line of the protractor at the vertex of the angle.
Naming and Measuring Angles Look at the scale, starting from 0,and read the size of the angle.
Naming and Measuring Angles Example • 60 degrees • 120 degrees
Naming and Measuring Angles Example • 75 degrees • 105 degrees
Naming and Measuring Angles Example • 30 degrees • 150 degrees
Naming and Measuring Angles Example • 50 degrees • 130 degrees