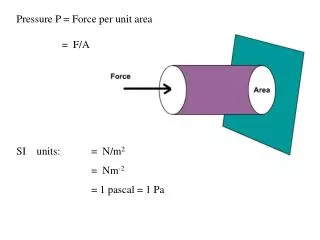
Force per unit area
340 likes | 590 Vues
Force per unit area. Density Buoyancy Pressure Power. 16 of 30. Mass per unit volume. Density Buoyancy Pressure Power. 20 of 30. Upward force experienced by an object immersed in a fluid. Density Buoyancy Pressure Power. 21 of 30.

Force per unit area
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Force per unit area • Density • Buoyancy • Pressure • Power 16 of 30
Mass per unit volume • Density • Buoyancy • Pressure • Power 20 of 30
Upward force experienced by an object immersed in a fluid. • Density • Buoyancy • Pressure • Power 21 of 30
The buoyant force experienced by an object equals the weight of the fluid it displaces. • Archimedes’ principle • Pascal’s principle • Bernoulli’s Law • The ideal gas law 19 of 30
Changes in pressure are transmitted throughout a fluid. • Archimedes’ principle • Pascal’s principle • Bernoulli’s Law • The ideal gas law 20 of 30
A Pascal is equal to one • Gram/cubic centimeter • Joule/second • Newton/square meter • Joule/kilogram/Kelvin 20 of 30
The ______ is equal on each cylinder of a hydraulic lift. • Pressure • Force • Area • Displacement 21 of 30
Density equals: • m/V • F/A • rVg • aLoDT 21 of 30
The buoyant force equals the ____ of the displaced fluid • Density • Mass • Volume • Weight 21 of 30
The average kinetic energy of a particle in random thermal motion describes • Heat • Thermal Energy • Mechanical Energy • Temperature 21 of 30
1.0 L of gas is initially at a temperature of -73oC and a pressure of 80 kPa. If the temperature is raised to 23oC with no change of volume the new pressure will be: • 27 kPa • 120 kPa • 160 kPa • 180 kPa 18 of 30
If a 24 kg object rests on a surface with an area of 0.08 m2 it exerts a pressure of: • 300 Pa • 3.0 kPa • 0.0033 Pa • 55 psi 21 of 30
Which formula could be used to solve a problem about hydraulic lifts? • P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 • DL=aLDT • P=Po + rhg • F1/A1=F2/A2 23 of 30
Which formula could be used to determine the pressure exerted by a fluid at a certain depth? • FB=rVg • r=m/V • P=Po+rhg • P=W/t 22 of 30
When heat is added to a substance at its melting point its temperature increases. • True • False 23 of 30
The increase in thermal energy needed to raise one unit of mass by one unit of temperature is called: • Heat of vaporization • Specific Heat • Coefficient of linear thermal expansion • Radiant Heat 19 of 30
23 of 30 The first law of thermodynamics states that: • The internal energy of a system can be increased by doing work or adding heat. • The bouyant force equals the weight of fluid displaced. • The entropy of the universe is always increasing.
23 of 30 The relationship between heat energy and temperature change is given by the formula: • Q=mcDT • DL=aLoDT • PV=nRT • P=W/t
23 of 30 When a chocolate bar is cut in half its density is… • Halved • Unchanged • Doubled
23 of 30 One kilogram of styrofoam has _____ density than one kilogram of iron • A smaller • A greater • The same
22 of 30 If a loaf of bread is compressed, its _____ • Mass decreases • Volume increases • Density increases • None of these
23 of 30 A wooden block has a mass of 800 g and a volume of 2 cm3. What is the block’s density? • 800 g/cm3 • 400 g/cm3 • 1600 g/cm3 • 0.4 g/cm3 • 0.025 cm3/g
22 of 30 Water pressure is greatest against the _____ • Top of a submerged object • Bottom of a submerged object • Sides of a submerged object • None of these
23 of 30 A completely submerged object always displaces an amount of fluid equal to its own: • Volume • Weight • Density • Mass
22 of 30 One liter of water has a mass of: • 1 kg • 1 N • Both of these • Neither of these
21 of 30 What is the buoyant force acting on a 34,000 N ship that is floating in the ocean? • Less than 34,000 N • 34,000 N • More than 34,000 N • Depends on the density of the sea water
19 of 30 What is the weight of water which is displaced by a floating 34,000 N ship? • Less than 34,000 N • 34,000 N • More than 34,000 N • Depends on the ship’s shape • Depends on the density of the seawater
21 of 30 An object that is partly or entirely immersed in a liquid is buoyed up by a force that is: • Equal to its own weight • Equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces. • Equal to the density of the fluid it is in. • Equal to the volume of the fluid it is in.
22 of 30 A rock suspended by a weighing scale weighs 5.0 N out of water and 3.0 N when submerged in water. What is the buoyant force acting on the rock? • 5.0 N • 3.0 N • 2.0 N • 8.0 N • None of these
21 of 30 Compared to an empty ship, the same ship loaded with styrofoam will float: • Higher in the water • Lower in the water • At the same level in the water.
23 of 30 A block of styrofoam floats on a lake while a block of lead with equal volume lies submerged at the bottom of the lake. The buoyant force is greatest on the: • Styrofoam • Lead • Is the same for both
22 of 30 A suction cup sticks to a wall. It is ____. • Pulled to the wall by the vacuum • Pushed to the wall by the atmosphere • Both of these • Neither of these