Origin, Evolution, and Composition of the Atmosphere
171 likes | 601 Vues
Origin, Evolution, and Composition of the Atmosphere. Abbreviation Definitions . Ga : billion years Ma: Million years H 2 O v : water vapor H 2 O l : Liquid water CO 2 : Carbon Dioxide N 2 : nitrogen molecule O 2 : oxygen molecule. Origins of Earth. Nebula Theory

Origin, Evolution, and Composition of the Atmosphere
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Abbreviation Definitions Ga: billion years Ma: Million years H2Ov : water vapor H2Ol : Liquid water CO2 : Carbon Dioxide N2 : nitrogen molecule O2 : oxygen molecule
Origins of Earth • Nebula Theory • Solar nebula, rotating proto-planetary disk, accretion = planetesimals = protoplanet = planets • Age of the Earth: 4.6 Ga
Possible sources of Earth’s present atmosphere • Volcanic outgassing • CO2 and H2Ov are the most abundant volcanic gases • Impact degassing • CO2 and H2O released during impacts of planetesimals as Earth accreted • Later impacts, especially by water-rich comets, during the heavy bombardment period (lasting to approx.. 3.8 Ga)
Phase 1: Primordial atmosphere • 4.6 Ga • Original nebula • Dominated by H, He , and hydrogen compounds (methane, ammonia) • Blown away by solar wind
Phase 2: Early secondary atmosphere • 4.6 to 2.0 Ga • Formed by impact degassing, outgassing, and/or comet impacts • N2, CO2, and H2Ov • H2Ov largely removed by 4.0 Ga as Earth cools • Formation of oceans due to cooling of H2Ov • Carbon dioxide is “rained out” of the atmosphere to be eventually stored in marine sediments/limestone • H2Ov→cooling→H2Ol =oceans
Phase 3: Transitional secondary atmosphere • 2.0 Ga to 400 Ma • Dominated N2 • Continued removal of CO2 by biological processes and storage in marine sediments • Build-up of O2 over time • Evolution of photosynthesis, maybe as early as 3.8 Ga • CO2 + H2O →Sunlight →Carbohydrate (C-H “food”) + O2
Figure 1http://www.windows2universe.org/life/images/oxygen_history_jpg_image.html
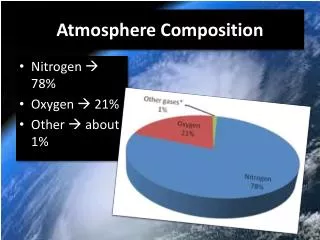
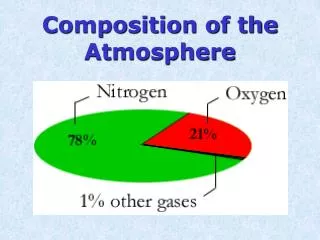
Phase 4: Modern atmosphere ~ 400 Ma to present Dominated by N2 and O2 Presents levels of oxygen Ozone layer formed Life colonizes the land