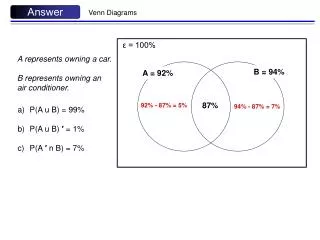
Answer
790 likes | 960 Vues
Answer. About 1.585 Gallons or about 6 liters. Today…. Circulation Short Movie http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=800CA676-82D2-4990-888A-DC098663721F&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US. Friday May 16 th 2014. QU: What is the purpose of the circulatory system?

Answer
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Answer • About 1.585 Gallons or about 6 liters
Today… • Circulation Short Movie • http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=800CA676-82D2-4990-888A-DC098663721F&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US
Friday May 16th2014 • QU: What is the purpose of the circulatory system? **YES YOU NEED YOUR BOOKS FOR THE REST OF THE YEAR!!** • OBJ: Circ. Clip, Blood Composition Notes “A child's heart is about the size of a clenched fist; an adult's heart is about the size of two fists.”
Your Circulatory System • Purpose: Carry oxygen and nutrients to cells, remove wastes (i.e. carbon dioxide) • Does this through a network of blood vessels
Chapter 30 Circulatory System
Arteries • Carries blood away from the heart towards the capillaries • Thick walls-can dilate or constrict • Controls pressure to ensure blood flows in one direction • Narrow=Higher pressure • Dilated=Lower pressure
Capillaries • Narrow-only one blood vessel through at a time • Walls are very thin-enables diffusion • nutrients and oxygen out of blood • Waste products into blood
Veins • Pick up blood from capillaries • Carries blood towards heart • Blood in veins is under very little pressure • Relies on muscle contractions and one-way valves to push blood back to heart.
Chemical Exchange • Diffusion: High to Low • Waste products taken in by blood • Oxygen and nutrients spit out by blood
So what is blood exactly?? • Considered connective tissue • Made up of cells and liquid parts “Under normal activity takes about 1 minute for all of your blood to flow through your body.”
Plasma • Makes up 55% of the blood • About 90% water
Red Blood Cells • Most numerous cells in your body • Carry oxygen from the lungs to your cells • Hemoglobin: What holds onto your oxygen
Red Blood Cells • Produced in the bone marrow • Shape increases surface area and the amount of oxygen it can hold “We make about 2 million per second”
White Blood Cells • Fight infection • When fighting an infection the number of WBCs increases
Blood Clotting • When you get a scrape your body stops the bleeding with a blood clot • Depends on small fragments of blood cells called platelets
Platelets • Break apart and release clotting factors that are sticky • This grabs other-builds a large network of platelets and RBCs • Stretches over the torn tissue. • Dries into a scab
So what is brought back to the heart? • We said that the circulatory system picks up waste right? • Where does it put that waste • It would be bad news if it dumped it in the heart So what happens?
Wastes • Your circulatory system picks up carbon dioxide, lactic acid and other wastes along the way. • It carries them along until it can get rid of them.
Where they are dropped off • Wastes are dropped off at: • Liver • Kidneys • Digestive System • Lymphatic System… Kidneys Liver
Lymphatic System • Blood flows through capillaries and drops off nutrients. • Blood can’t leave the capillaries • The nutrients are carried in a fluid called LYMPH
Monday May 19th2014 • QU: Describe the function of the red blood cells. *Homework: Functions of the Heart Due Monday* • OBJ: Waste Notes, Systemic and Pulmonary Systems “In your lifetime, you'll shed over 40 pounds of skin.”
Tuesday May 20th2014 • QU: Why is blood doping effective? (and illegal) *Chapter Review Due Tomorrow, Circulatory Test Tomorrow* • OBJ: Parts of the Hearts and Functions “Mars’ red color is due to iron oxide, also known as rust, and has the consistency of talcum powder.”
Heart Dissection • If you goof around, you will be sitting back at your desks. • Do not do anything to harm the hearts they are very expensive. • Each table has pins, a probe, a tray, and masking tape. • Each table looks spotless. This is how they should look at the end of the hour.
Heart Dissection • You will need my signature for placing the pins in the correct spot. • BE GENTLE!
Blood Doping • Remove blood • Return plasma • Save RBCs for later • Let body make more RBCs • Then before event replace blood • Increases amount of hemoglobin in blood • Better at carrying oxygen • More oxygen to organs=better performance
WedNesdayMay 21st 2014 E • QU: You do not need to draw the picture. • OBJ: Check in Homework, Heart Lab “The surface area of the human lungs is equal to that of a tennis court.” A C B D
Heart Beat • 1st sound (the lub): Atria Contracting • 2nd sound (the dub): Ventricles Contracting • How does your heart know to open and close the valves?
Pacemaker • Region of your heart muscle • Sets pace of your heart beat • Sends electrical signals as the message for contractions • First hit SA Node: Causes atria to contract • Then AV Node: Slows message down (giving time to atria to relax) • Then His-Purkinje Network: Causes Ventricles to contract http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SMXBR_YFocs 22secs-1.42
Path way of blood • Aorta • Body Capillaries-Lose Oxygen, Gain CO2 • Superior Vena Cava, Inferior Vena Cava • Right Atrium • Right Ventricle • Right Pulmonary Artery, Left Pulmonary Artery • Right Lung, Left Lung-Gain Oxygen, Lose CO2 • At the alveoli after the oxygen is inhaled • Right Pulmonary Vein, Left Pulmonary Vein • Left Atrium • Left Ventricle • Aorta
Question 1 • What carries blood away from the heart? • Veins • Arteries • Capillaries
Question 2 • What carries blood towards the heart? • Veins • Arteries • Capillaries
Question 3 • What makes up 55% of our blood? • RBCs • WBCs • Plasma
Question 4 • What is plasma mostly made up of? A. Water B. Nutrients C. Proteins
Question 5 • What is responsible for starting the formation of a scab? A. RBCs B. Fibrin C. Platelets
Question 6 • What is the purpose of the circulatory system? • Circulate oxygen and nutrients • Remove wastes • Both of the above are correct
Question 7 • What is the largest artery in the body? • Pulmonary Artery • Aorta
Question 8 • What is responsible for receiving the blood from outside the heart? • Ventricle • Atrium
Question 9 • What is responsible for sending the blood out of the heart? • Ventricle • Atrium
Question 10 • What side of the heart contains deoxygenated blood? • Right • Left
Question 11 • What part of the heart is responsible for separating the deoxygenated blood from the oxygenated blood? • Valves • Septum • Neither of the above
Question 12 • Which circuit includes the lungs? • Pulmonary • Systemic
WedNesday May 21st 2014 • QU: Describe how the blood leaves your left ventricle, loses oxygen and then is re-oxygenated. *Circulatory Test Thursday • OBJ: Over Heart Lab, Organize Binder, Ch Review “The world's largest amphibian is the giant salamander. It can grow up to 5 ft. in length.”
Thursday May 22nd 2014 • QU: How did you study for this test? *Chap Review Due Today* • OBJ: Circulatory System Test “You can reduce your home energy use by 5% by replacing your dryer with a clothesline” –Sierra Club
Respiratory System Chapter 30
Respiratory System • Function: Provide oxygen for distribution to cells through your body as well as remove the waste product carbon dioxide.