Modern Communication Evolution: SDR in Mobile Networks
160 likes | 200 Vues
Explore the evolution of modern communication through Software Defined Radio (SDR) in mobile networks. Discover cutting-edge technologies like GSM, Internet, and 3G integration. Learn about efficient packet-switching methods, RF system design, and CDMA fundamentals. Dive into macro and micro cell specifications, power control, and RAKE receivers. This seminar focuses on the latest advancements in wireless voice services and how SDR is shaping the future of mobile communication. References include prominent experts in the field and case studies on SDR applications in 3G networks.

Modern Communication Evolution: SDR in Mobile Networks
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SDR for mobile communication M . R . Azimi Course seminar for SDR Instructor : Dr Omidi
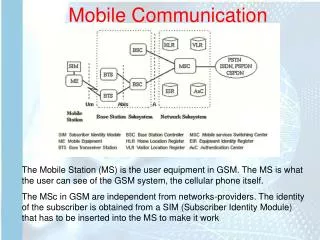
Modern communication : wireless voice service • Leading edge of this revolution : GSM • Simultaneous phenomenon : Internet • Leading edge of this phenomenon : www ,web browser, TCP/IP • New idea : integrate both of them third generation
Common methods for providing BWM • HSCSD : symmetric or asymmetric aggregates circuit channels • GPRS: sharing time slots between different users and enabling Internet access • EDGE modifies the radio link modulation from GMSK to 8QPSK • UMTS utilizes a wide band CDMA or TD/CDMA transceiver
UMTS • All mentioned methods using circuit switching: - inefficient for bursty traffic - scheduler at RNC , slow resource allocation -slow update for SHO during cell selection.
UMTS • New approach : using packet switching , adding all IP features , HSDPA, intelligent or adaptive antenna - a spectrum efficient packet-by-packet fast scheduling - Fast Resource Allocation with the scheduler at the BTS - FCS due to the optimization for packet data delivery, capacity coverage and high data rate at the cell edge
RF system design • Noise and channel capacity : • Free space loss : • Loss in non L.O.S : • Outdoor to indoor and pedestrian model :
RF system design • Receiving power in two models: - left figure : -right figure: for point B: for point D:
A/D , D/A • First nyquist rule , BP sampling , over sampling • Anti aliasing filter : SAW filter • successive approximation, multipass architecture ,dithering • clock jitter and aperture uncertainty - ADC with an rms sample clock timing jitter of
ADC noise budget : • DAC noise budget:
DUCs , DDCs • DDC’s requirements in 2G and 3G: -Filter or isolate a narrow band of frequencies from the wideband source and reject the reminder of the band. -Translate that isolated carrier down in frequency ,usually from an IF to baseband. -Reduce the data rate to some integer multiple of information rate. • DUC’s requirements in 2G and 3G: -translate one or more narrowband signal sources up in frequency, usually from baseband to an IF. -Combine the baseband sources to create one wideband result. -Increase the data rate to a digital IF rate.
ISL5217(DUC) • Data input routing • Data modulation • Sample rate NCO • Shaping filters • Halfband filter • Complex mixer and carrier NCO • Gain control • Output routing, summing and control
CDMA fundamentals • Spreading • Multiple access • soft handoff • power control • RAKE receiver
Macro cell specifications • Macro cells : high reliability and providing fall-back capacity
Micro cell specifications • High user density , lower power RF power amplifier
References: • software defined radio for 3G “ Paul burns “ • The UMTS Network and Radio Access Technology “Dr. Jonathan P. Castro “Orange Communications SA/AG, Switzerland • “Communication Profiles for SDR Equipment” by Eiman Mohyeldin, Markus Dillinger, and J. Luo, Peter Dornbusch, Michael Fahrmair, Chris Salzmann, Siemens AG, Munich University of Technology • Software radio evolution and its application to aeronautical mobile communications by ”Minh Nguyan” • Software Defined Radio Forum General Meeting by Nalini Uhrig ,Bryan Tropper,Nancy Pearson, Michael Agha