Hormones
190 likes | 613 Vues
Hormones. Noadswood Science, 2011. Hormones. To know how hormones are used in the body, and how these control the menstrual cycle. Hormones. Hormones are chemicals secreted by glands in the body.

Hormones
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hormones Noadswood Science, 2011
Hormones • To know how hormones are used in the body, and how these control the menstrual cycle
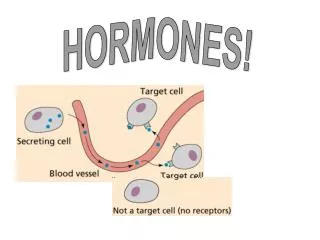
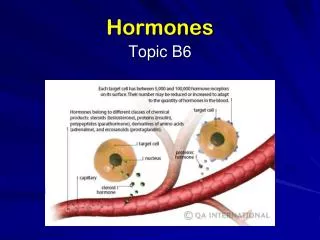
Hormones • Hormones are chemicals secreted by glands in the body • Different hormones affect different target organs, with the bloodstream transporting hormones from the glands to the target organs…
Menstrual Cycle • The menstrual cycle in women is a recurring process in which the lining of the uterus (womb) is prepared for pregnancy, and if pregnancy does not happen, the lining is shed at menstruation • Several hormones control this cycle, which includes controlling the release of an egg each month from an ovary, and changing the thickness of the uterus lining • These hormones are secreted by the ovaries and pituitary gland
Menstrual Cycle • The menstrual cycle begins at day 1, when bleeding from the vagina begins. This is caused by the loss of the uterus lining (with some blood) - this is known as menstruation, or having a period (lasting 3-7 days) • By around day 5 menstruation stops. The lining of the uterus begins to re-grow, and an egg cell starts to mature in one of the ovaries • Around day 14 the mature egg cell is released from the ovary. This is called ovulation - the egg cell travels down the oviduct towards the uterus
Menstrual Cycle • If the egg cell does not meet with a sperm cell (no fertilisation) then the lining of the uterus begins to break down again, and the cycle repeats • BUT - if the egg cell meets and joins with a sperm cell (fertilisation) then it attaches to the lining of the uterus and the female becomes pregnant - at this point the cycle stops
Menstrual Cycle Day 1 - menstrual cycle and menstruation (period) begins (lasts 3-7 days) Day 3-7 - menstruation (period) stops Day 14 - an egg cell is released from one of the ovaries (ovulation) Day 28 - if the egg has not been fertilised (by a sperm), the cycle repeats
Menstrual Cycle • Complete the menstrual cycle worksheet, sticking all the sections into your book
Menstrual Cycle • If an egg is fertilised between days 15-28, the menstrual cycle will stop • Fertile means the female has the ability to become pregnant (greatest chance of conception) • Probably ~ 28 days later: 4th December (although this can be a few days before / after) Menstruation (period) Uterus lining breaks apart without progesterone Most fertile time The egg cell is swept along the oviduct towards the uterus Egg maturation FSH released – egg cell starts to mature in ovary and the uterus lining builds up Ovulation The egg cell is released from the ovary – caused by LH
FSH • The hormone FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) is secreted by the pituitary gland • FSH makes two things happen: - • It causes an egg to mature in an ovary • It stimulates the ovaries to release the hormone oestrogen
Oestrogen • The hormone oestrogen is secreted by the ovaries • Oestrogen makes two things happen: - • It stops FSH being produced - so that only one egg matures in a cycle • It stimulates the pituitary gland to release the hormone LH
LH • The hormone LH (luteinisinghormone) causes the mature egg to be released from the ovary • Knowing when LH has surged can be useful when trying to conceive as this informs you of when ovulation has occurred
Progesterone • Progesterone is secreted by ovaries, maintaining the lining of the uterus (levels stay high during pregnancy)
Controlling Fertility • Human fertility is controlled by hormones – a knowledge of hormones can be used to decide to increase, or reduce, the chances of fertilisation and pregnancy • The oral contraceptive, 'the pill', greatly reduces the chances of mature eggs being produced • The pill contains oestrogen and progesterone which inhibit the production of FSH, which in turn stops eggs maturing in the ovaries
Fertility Treatment • Some women have difficulty becoming pregnant because they don't produce enough FSH to allow their eggs to mature – ‘fertility drugs' contain FSH, which stimulates eggs to mature in the ovary • Fertility treatments increase a woman's chance of becoming pregnant, although the treatment may not always work • On the other hand, because the treatment boosts the production of mature eggs, multiple conceptions sometimes occur, with twins or triplets being expected, increasing the risk of complications in pregnancy and childbirth
IVF • If a couple are having difficulty conceiving a child because the quantity or quality of the man’s sperm is poor then in vitro fertilisation (IVF) can be used • This is where the egg is fertilised outside the woman’s body and then implanted back into her uterus • As FSH can also be used to encourage the production of several mature eggs at once, it is used as part of IVF to increase the number of eggs available for fertilisation