Kingdoms
100 likes | 333 Vues
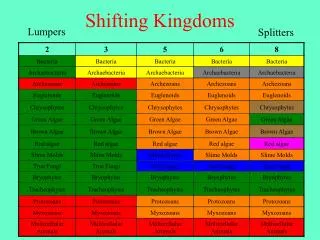
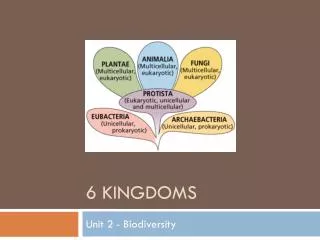
Kingdoms. Viruses and Bacteria. 6 Kingdoms. The 6 kingdoms are divided among 3 domains based on general cell structure Bacteria – E ubacteria Archaea – Archaebacteria Eukarya – Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists. Where do viruses fit in the ‘Tree of Life’?.

Kingdoms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Kingdoms Viruses and Bacteria
6 Kingdoms • The 6 kingdoms are divided among 3 domains based on general cell structure • Bacteria – Eubacteria • Archaea – Archaebacteria • Eukarya – Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists
Where do viruses fit in the ‘Tree of Life’? • Although viruses have some characteristics of living things, • they are not made of cells • cannot reproduce on their own • They are not considered ‘living’
Viral Replication • If virus is in lysogenic cycle, host may not be aware they are infected. • Viruses are usually only transmitted during lytic cycle
Archaebacteria • “Archaea” = Ancient • Believed to be the fist species on Earth • Most are anaerobic – live without oxygen • Well-suited to extreme environments • Acidophiles – live at pH <3 • Thermophiles – live at very high temp (>100°C) • Halophiles – live in areas with high salt
Archaea and Eubacteria • All bacteria share a number of common characteristics: • All prokaryotic • All single-celled • All have a single chromosome • All reproduce asexually through binary fission • Primary difference between kingdoms is related to presence or absence of peptidoglycan in cell wall • Present = Eubacteria • Absence = Archaea
Classifying Eubacteria • Eubacteria are classified according to their arrangement and shape:
Independent Work • Read Pages 343-346 • Benefits of Bacteria – how are they helpful in the human body? How are they used in pollution control? • Harmful effects – How do bacteria cause symptoms of disease? How are bacterial infections passed from one person to another? • Antibiotic resistance – how do bacteria acquire resistance to antibiotics? (note: ‘conjugation’ = sharing of genetic info between bacteria ↓)