Understanding An Aging Population
260 likes | 504 Vues
Understanding An Aging Population. Keirsten D. Montgomery University of Pittsburgh: School of Nursing Spring 2003. Objectives. Demographics Understanding target population Statistical Data Understanding scope of the problem Risk Factors Falls Prevention Related literature and data.

Understanding An Aging Population
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Understanding An Aging Population Keirsten D. Montgomery University of Pittsburgh: School of Nursing Spring 2003
Objectives • Demographics • Understanding target population • Statistical Data • Understanding scope of the problem • Risk Factors • Falls • Prevention • Related literature and data
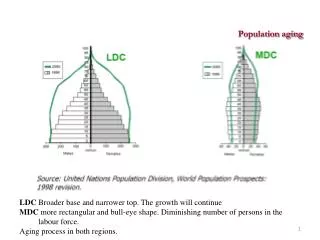
The Aging Population • Dramatic increases in aging population from 1996 to projected 2025 • Age 60 – 64 • 1996: 70 million • 2025: 100 + million • Age 80+ • 1996: 30 million • 2025: 80 million US Department of Commerce: Economics and Statistics Administration Global Aging into the 21st Century – 2000
The Graphic Triangle US Department of Commerce: Economics and Statistics Administration Age: 2000 – 2000 Brief
The Oldest Old • The oldest old has the fastest growing population trends • 85+: 38% between 1996 and 2000 US Department of Commerce: Economics and Statistics Administration The 65 years and over population – 2000 Brief
Geographical • Proportions of 65+ population by state • Florida (18%) • Pennsylvania (16%) • West Virginia (15%) • Iowa (15%) • North Dakota (15%) • Rhode Island (15%) US Department of Commerce: Economics and Statistics Administration Age: 2000 – 2000 Brief
The State Breakdown US Department of Commerce: Economics and Statistics Administration Age: 2000 – 2000 Brief
Disability Statistics • 1 in 5 Individuals will suffer from some kind of disability • Data shows that half of senior 65 + have a disability US Department of Commerce: Economics and Statistics Administration Disabilities Affect One-Fifth of all Americans – 2000 Census Brief
Fall Risk In The Elderly WISQARS injury report forms – http://www.cdc.gov/ncipc/default.htm
Fall Risk Assessment Associated Press (2003) Researchers study why elderly fall, ways to minimize damage. The Winston Salem Journal
Fall Risk Assessment Rubenstein; Powers & MacLean. (2001). Quality indicators for the management and prevention of falls and mobility problems in vulnerable elders. Annals of Internal Medicine
Physical Age Cognitive impairments Visual impairments Muscle weakness Gait and balance disturbances Fall History Risk Factors • Jensen; Lundin-Olsson; Nyberg & Gustafson. (2002). Fall and injury prevention in older people living in residential care facilities: A cluster randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine • American Geriatrics Society, British Geriatrics Society, and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Panel on Falls Prevention. (2001). Guideline for the prevention of falls in older persons. The Journal of the American Geriatrics Society • Rubenstein; Powers & MacLean. (2001). Quality indicators for the management and prevention of falls and mobility problems in vulnerable elders. Annals of Internal Medicine
Risk Factors • Medical • Polypharmacy • Orthostatic Hypotension • Stroke or Myocardial infarction • Parkinson’s disease • Arthritis • Osteoporosis • Psychiatric conditions • Urinary incontinence • Jensen; Lundin-Olsson; Nyberg & Gustafson. (2002). Fall and injury prevention in older people living in residential care facilities: A cluster randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine • American Geriatrics Society, British Geriatrics Society, and American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons Panel on Falls Prevention. (2001). Guideline for the prevention of falls in older persons. The Journal of the American Geriatrics Society • Rubenstein; Powers & MacLean. (2001). Quality indicators for the management and prevention of falls and mobility problems in vulnerable elders. Annals of Internal Medicine
Risk Factors • Environmental • Poor lighting • Loose rugs • Beds/toilets without handrails • Surface preparation • Physical/perceived obstacles • Jensen; Lundin-Olsson; Nyberg & Gustafson. (2002). Fall and injury prevention in older people living in residential care facilities: A cluster randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine • American Geriatrics Society, British Geriatrics Society, and American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Panel on Falls Prevention. (2001). Guideline for the prevention of falls in older persons. The Journal of the American Geriatrics Society • Rubenstein; Powers & MacLean. (2001). Quality indicators for the management and prevention of falls and mobility problems in vulnerable elders. Annals of Internal Medicine
Results of Falls • Hospitalization • Premature Nursing Home Placement • Increased dependency • Assisted living • Self Imposed • Feelings of Inadequacy Rubenstein; Powers & MacLean. (2001). Quality indicators for the management and prevention of falls and mobility problems in vulnerable elders. Annals of Internal Medicine
Staff Education Evaluation Exercise Environmental Modifications Assistive Devices Supply or Repair Assistive Devices Change in Medication Regimen Fall Prevention Strategies Rubenstein; Powers & MacLean. (2001). Quality indicators for the management and prevention of falls and mobility problems in vulnerable elders. Annals of Internal Medicine
Choosing An Ambulation Aid Sloan; Haslam; and Foret. (2001). Teaching the use of walker and canes. Home Healthcare Nurse
Aging Population’s Rejection of Walkers and Assistive Devices • Emphasize qualities which they consider demeaning to the person • Aging, diminishing competence, dependence • Believe falls are inevitable • No perception of need (Denial) • PRIDE • Lack feeling’s of safety while using assistive devices • COST Aminzadeh & Edwards. (1998) Exploring senior’s view’s of the use of assistive devices in fall prevention. Public Health Nursing
Actual Responses: Healthcare Workers and Seniors Aminzadeh & Edwards. (1998) Exploring senior’s view’s of the use of assistive devices in fall prevention. Public Health Nursing
General Characteristics of a Walker • Use • Weak, elderly individuals who present with mild balance problems • Purpose • Widens the base of support • Transfers weight bearing to upper extremities • Allows extra-sensory and proprioceptive feedback • Types • Standard or two/four wheeled walkers Sloan; Haslam; and Foret. (2001). Teaching the use of walker and canes. Home Healthcare Nurse
General Characteristics of a Walker • Advantages • Increased stability, support • Elderly do not imply “age” stigma • Misuses • Improper Height • Improper Use • Improper sit – to – stand transfers • Improper Use on Stairs Sloan; Haslam; and Foret. (2001). Teaching the use of walker and canes. Home Healthcare Nurse
Data on Injuries Related to Walker • Data found relates to malfunctioning apparatus on walker • Example: A PT FELL DUE TO A WALKER LEG BREAKING DURING USE. THIS INCIDENT ALLEGEDLY RESULTED IN A BROKEN HIP AND CRACKED RIB • Data does exist to support suggestion that walkers can be the obstacle • Example: AN 81-YR-OLD, 150 LB, FEMALE PT TURNED SIDEWAYS, FELL AND TIPPED OVER IN AMBULATOR. WAS NOT BEING MONITORED AT TIME OF EVENT. PT WAS NOT HURT AND DID NOT NEED MEDICAL HELP. PT HAS ALZHEIMER'S. DEVICE NOT RETURNED. MFR DATE APPROX 5/93 http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfmdr/search.CFM