Plate Tectonics
260 likes | 459 Vues
Plate Tectonics. It’s a pretty zany idea What brought it about? Geologic observations made by Wegener and first suggested in 1915 Why is it important?. Types of Evidence for Continental Drift. Geographic Evidence. Fossil Evidence. Types of Evidence for Continental Drift.

Plate Tectonics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Plate Tectonics • It’s a pretty zany idea • What brought it about? • Geologic observations made by Wegener and first suggested in 1915 • Why is it important?
Types of Evidence for Continental Drift Geographic Evidence Fossil Evidence
Types of Evidence for Continental Drift Evidence from Glacial Deposits Evidence from Coal Deposits
Magnetic Evidence The Earth’s magnetic field can be: Normal: Compass points North Reversed: Compass points South The direction of the magnetic field is recorded by rocks as they form Patterns of reversal are nearly mirror image
AnimationFrom Smith and PunSea Floor Spreading andSea Floor Magnetism skip
How Plates Behave (Bean pot analogy) Smith and PunPlate Motions Through Time
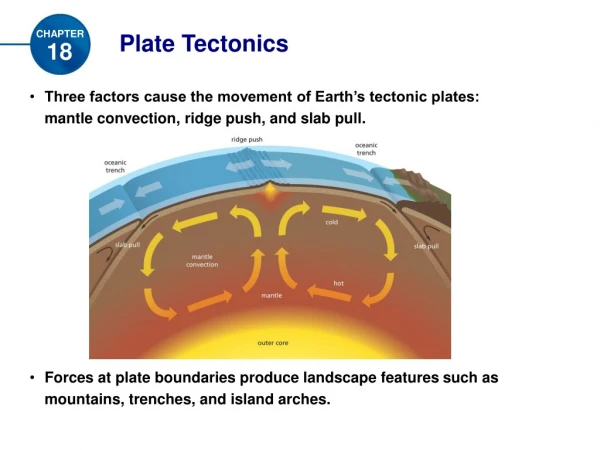
The Plates The plates are essentially RIGID pieces of the Earth’s crust They move due to convection of the mantle They can contain both OCEANIC and CONTINENTAL crust Passive Margin Active Margin (Plate Boundary)
Thick Pine Thin Pine Thin Oak H T D Isostacy D=kT Depth below waterline H=(1-k)T Height above waterline k= rB/rW Fraction of block below water line
Three Basic Types of Plate Boundaries • Divergent - plates moving away from one another (Tension) • Convergent - plates moving toward one another (Compression) • Transform - plates moving past one another (Shear) ! Most plates include con/divergent and transform components !
Smith and PunSea Floor Spreading and Sea Floor MagnetizationMotion at Divergent Boundaries skip
Formation of Oceanic Crust Sediments Pillow lavas Sheeted dikes Gabbro Peridotite (Mantle rock)
midocean RIDGES Cooler More Dense Lower Hotter Less Dense Higher Cooler More Dense Lower
Smith and PunForming a Divergent BoundaryANIMATION20 - Plate Divergence
Convergent Boundaries • Oceanic crust is denser and “rides lower” than continental crust • Expect different things to happen • Ocean-Continent Collisions • Continent Continent Collisions Trenches Mountains
Animations • Subduction • Animation 20- Ocean-Continent • Animation 20- Continent-Continent
Transform Boundaries • San Andreas Fault in California • Animation 20-Transform Boundaries • Transform Faults in Midocean Ridges • Motion at a transform plate boundary
Hotspots • Smith and Pun: Hotspots and Plumes