Mediastinum and Diaphragm
490 likes | 2.62k Vues
Mediastinum and Diaphragm . Dr. A. S. PITAKE Department of Anatomy USM-KLE IMP. Thoracic Mediastinum : is septum or space between two lungs(pleural sacs) . Boundaries . Superiorly : thoracic inlet Inferiorly :diaphragm

Mediastinum and Diaphragm
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mediastinum and Diaphragm Dr. A. S. PITAKE Department of Anatomy USM-KLE IMP
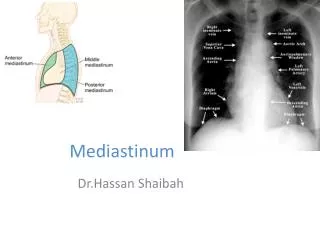
Thoracic Mediastinum : is septum or space between two lungs(pleural sacs)
Boundaries • Superiorly : thoracic inlet • Inferiorly :diaphragm • In the sides: lungs with mediastinal surfaces of pleura • Infront : sternum • Behind : T1to T12 vertebrae with IVD
Sub divisions: A)superior B) Inferior : 1)Anterior 2 ) Middle 3) Posterior
Superior mediastinum • Superiorly:Thoracic inlet • Inferioly :Plane at sternal angle &lower border ofT4 In front : Manubrium sternum • Behind : T1to T4 vertebrae &IVD
Contents of sup mediastinum • Divided into :Three • 1)Retrosternal • a) Thymus gland • b)sternothyroid& • sternohyoid muscle • c)Rt & Lt bracheocephalic vein • d) superior vena cava
2)Intermediate : • a)Arch of Aorta • b)Phrenic,vagus,cardiac nerves 3)Prevertebral :a)Trachea • b)Oesophagus • c)Thoracic duct • d)Lt recurrent laryngeal nerve • e)Origin of longus coli
Anterior mediastinum • Boundaries • Superiorly:imaginary • plane • Inferiorly :diaphragm • Anteriorly :sternal • body • Poteriorly :pericardium
Contents of ant mediastinum • 1)Superior sterno pericardial ligament • 2)Inferior sterno pericardial ligament • 3) Loose areolar tissue • 4)Retrosternal lymph nodes • 5)Mediastinalbrs of internal thoracic artery
Middle mediastinum most widest & largest sub division Boundaries: It is occupied mainly by heart & pericardium , limited on each side by mediastinal pleura
Contents of middle mediastinum • 1)Pericardium & heart • 2)Four pulmonary veins • 3)superior vena cava • 4)Arch of azygous vein • 5 )Tracheal bifurcation • 6)Lt & Rt bronchi • 7)Cardiac plexus of nerves • 8)Phrenic nerves • 9)Tracheobronchial Lymph nodes
Posterior mediastinum longest of sub divisions • Boundaries Superiorly: imaginary plane Inferiorly : diaphragm Anteriorly : tracheal bifurcation,pericardium pulmonary vessels,diaphragm Poteriorly :lower, T5 to T12 &IVD
Contents of posterior mediastinum Longitudinal structures- Oesophagus,Descending thoracic aorta,azygous and hemi azygous veins, thoracic duct,vagusnerve,splanchnic nerves. Transverse structures-Termination of accessory hemiazygousand hemiazygousvein,deviation of thoracic duct,posterior intercostal arteries and veins.
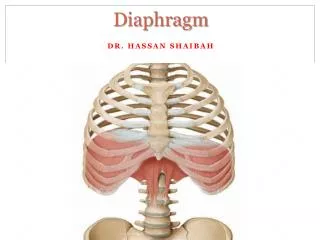
Diaphragm • It is chief muscle of respiration Definition-It is a dome shaped musculoaponeuroticpartition, which intervenes b/w the thorax and the abdomen. • It covers thoracic outlet
Origin of diaphragm Divided into three Sternal-Two slips from back of the xiphoid process Costal- inner surface of the lower six ribs and their costal cartilages. Vertebral- From right and left crura,right is longer than left and arises from the front of the bodies and intervertebral disc of upper three lumbar vertebrae. Left-crus- arises from bodies and intervertebral discs of upper two lumbar vertebrae. Both the crura are connected in the median plane by a Median arcuateligament.
Diaphragm origin It also arises from pair of medial &lateral arcuate ligaments ligaments
Insertion of diaphragm • Inserted into central tendon
Details of major opening • Aortic : • Level - T12 • Structures –abd aorta ,thoracic duct ,azygous vein • Oesophageal : • Level –T10 • Structures –oesophagus,vagaltrunks,brs of left gastric artery &lymphatics • Vena caval: • Level –T8 • Structures –vena cava ,brs of Rt phrenic nerve
Blood supply 1)Musculo-phrenic and pericardiophrenic arteries are the branches of the internal thoracic artery. 2)Lower 5 or 6 Posterior intercostal arteries. 3)Superior phrenic artery, is a branch from descending thoracic aorta. 4)Inferior phrenic arteries branches from abdominal aorta. All the veins corresponds to artery and drains into systemic veins.
Nerve supply Motor supply-phrenic nerve( c3,c4,c5) Sensory supply- Central part from phrenic nerves & peripheral part by lower 6-7 intercostal nerves. Sympathetic supply- From coeliac plexus to maintain the tone of the diaphragm.
Actions • It is a chief muscle of inspiration. when it contracts the ribs are fixed , vault of diaphragm descends , vertical diameter of thorax increases. • Helps in reflex actions like parturation,cough,micturation,vomiting etc. • Created pressure on vein , which increases the venous return.
Applied anatomy • 1)Hic cough • 2)Reffered pain • 3)Paralysis of diaphragm • 4)Hernias