Joints
170 likes | 503 Vues
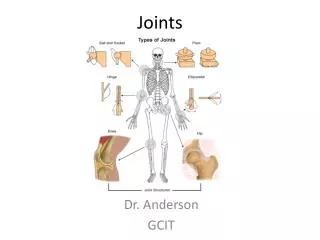
Joints. Major Joint Classifications. Synarthrodial Amphiarthrodial Cartilage Ligament Diarthrodial. Diarthrodial Joints. Characteristics Joint Capsule. Diarthrodial Joint Types. Gliding Hinge Pivot Condyloid Saddle Ball and Socket. Range of Motion of Joint Type .

Joints
E N D
Presentation Transcript
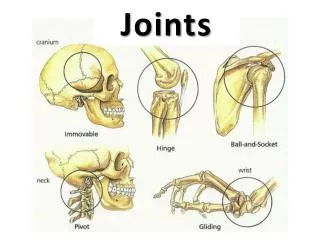
Major Joint Classifications • Synarthrodial • Amphiarthrodial • Cartilage • Ligament • Diarthrodial
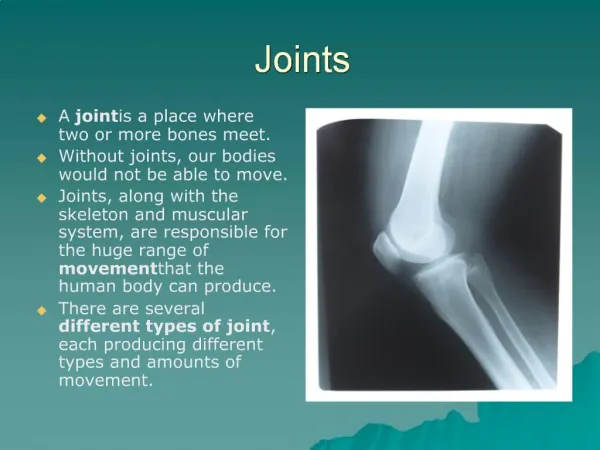
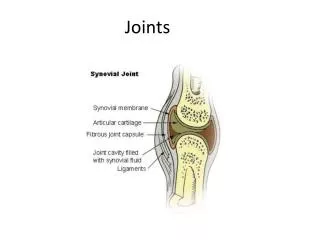
Diarthrodial Joints • Characteristics • Joint Capsule
Diarthrodial Joint Types • Gliding • Hinge • Pivot • Condyloid • Saddle • Ball and Socket
Range of Motion of Joint Type • Anatomical Compromises • some sacrifice mobility for stability • some sacrifice stability for mobility • Flexibility
Planes of Movement • Three primary planes • Sagittal • Frontal • Transverse
So How Can Knowledgeof Planes Help Us? • More effectively determine cause(s) of (sport) injury • More effectively correct poor movement practices • More effectively...
Axis of Rotation • The line formed by the intersection of the two planes NOT involved in the movement. • Perpendicular to Plane of Movement.
Levers • Machines • composed of a rigid bar and a fulcrum. • eg. of rigid bar? • eg. of fulcrum?
Levers • 3 Classifications • 1st Class - • 2nd Class - • 3rd Class -
Articular (Hyaline) Cartilage • Location: Covers articulating ends of bones (in synovial joints) • Purposes: • decrease friction • decrease load
Characteristics of AC • Highly Specialized • Can withstand relatively rigorous joint environment without failure. • Isolated tissue • Assists fitting of bone ends
Importance of AC • Least understood tissue in the body • Known Information: • Limited capacity for self-repair • does not follow Wolff’s Law (as we know it)
Factors affecting Breakdown of AC • High load • total number of stress peaks • changes in the intrinsic molecular and microscopic structure of AC • changes in its mechanical properties
How does Breakdownof AC occur? • loosens the collagen matrix • decrease in stiffness • increase in permeability
Special Cases • Disruption of Load carrying capacity of AC • Knee Meniscectomy • Ligament Rupture • Abnormal Joint Articulation • Cartilage degeneration • Excessive loads and load distribution disruptions
Joint Degeneration • Sport Examples: