Demand
490 likes | 743 Vues
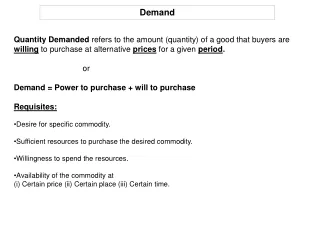
Demand. Chapter 4, Section 1, 2. What is “Demand?”. Willingness to buy a product and ability to pay for it. Demand Schedule. List of quantity that will be demanded for different market prices. P R I C E. D E M A N D. Law of Demand.

Demand
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Demand Chapter 4, Section 1, 2
What is “Demand?” • Willingness to buy a product and ability to pay for it.
Demand Schedule • List of quantity that will be demanded for different market prices.
PRICE D E M A N D Law of Demand • Quantity demanded and price have inverse relationships. • As price falls, consumers buy more.
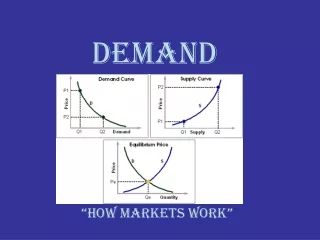
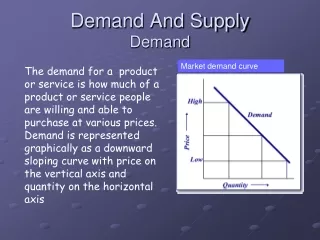
Demand Curve • Graph that shows how much will be purchased at each price. • Graph points on D Schedule
Quantity Demanded • Points on the curve • Show how much demanded at ONE price.
Application pg 101& 103 • Create a demand schedule showing how many pizzas you would buy per month at the following prices: $25, $20, $15, $10, $5 • Graph those points and draw the demand curve.
Changes in “qd” • “change in the # products consumers buy because of a change in price.”
Change in Demand • What conditions would arise to make you change (increase or decrease) your desire to buy a product? • When conditions change, the entire demand curve changes.
Changes in Demand • Consumer Taste • Change in style • Consumer Income • Change $ people make • Substitutes • Compliments
Price of Substitute • Substitutes – products that can be used in place of another product.
Price of Compliments • Compliment – two products used together
Elasticity of Demand Chapter 4, Section 3
Elasticity of Demand • Describes how responsive consumers are to price changes.
Elastic Demand • Elastic – when changing price has a large change in quantity demanded.
Inelastic Demand • Inelastic – change in price makes a small change in quantity demanded.
Pricing Policies • Governments tax inelastic goods because the increase in price does not change the quantity demanded.
Determinants What determines Demand Elasticity?
Yes No Yes No No No Yes =elastic No = inelastic Small Small Large Small Small Large Large =elastic Small = inelastic Lux. Nec. Lux. Nec. Nec. Lux. Luxury =elastic Necessity = inelastic Elast. Inel. Elast. Inel. Inel. Elast.
Demand Poster • Pick a product • Create a Demand Schedule using at least 6 different prices. • Draw your Demand Curve • Identify 2 Quantity Demanded Points • Describe a situation where DEMAND would increase or decrease. • Illustrate the change in Demand on your curve. • Identify how Elastic or Inelastic Demand for your product is using a continuum.
Supply Chapter 5
Supply • Willingness and ability of producer to offer goods for sale.
Supply Schedule • Table that shows how much a producer will offer for sale at market prices.
PRICE SUPPLY Law of Supply • Price and Supply have a parallel relationship • Producers are willing to sell more at a higher price.
Supply Curve • Graph that shows how much a producer will offer at each price.
Quantity Supplied • A point on the curve. • How much supplied at ONE price.
Change in Qs • “change in the # products producers are willing to sell because of change in price.”
Change in Supply • When something makes producers offer different amounts for sale at every price.
Input Cost • Increase or decrease in cost of the factors of production.
Technology • New technology decreases the cost of production.
Number of Sellers • More sellers = more supply
Elasticity of Supply • Elastic - changes in price cause large change in quantity supplied. • Inelastic – change in price causes small change in qs.
Equilibrium Price • Market price when qs = qd.
Surplus • Qs > Qd
Shortage • Qs < Qd
Price Ceiling • Maximum price sellers can charge. • Set below equilibrium • Shortage will occur.
Price Floor • Minimum price buyers must pay for product • Set above equilibrium • Surplus will result.