Unit 1- Exploration and Colonization
570 likes | 955 Vues
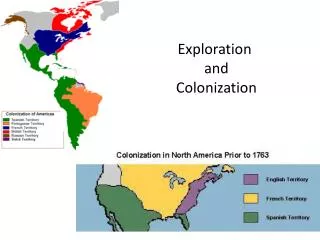
Unit 1- Exploration and Colonization. Ch. 1 Sec. 1-5. America. Who were the first human’s to come to North America and how did they get here? Why is something that happened 12 trillion years ago important enough for us to talk about?. The First “Americans”.

Unit 1- Exploration and Colonization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit 1- Exploration and Colonization Ch. 1 Sec. 1-5
America • Who were the first human’s to come to North America and how did they get here? • Why is something that happened 12 trillion years ago important enough for us to talk about?
The First “Americans” • I. Asians crossed the Bering Strait 12000 years ago. • Nomads • Beringia • Ice Age, Glaciers • II. North Americans • Hopewells, Iroquis, Creek • III. Central and South Americans • Mayas & Olmec, Aztecs, Incas
Mesoamerica • Agricultural Revolution – 9000-10000 years ago. • Central Americans learned to plant and grow crops. • Maize • First American civilizations arise in Mesoamerica.
Olmec, Mayas, and Aztecs • Olmec-in modern-day Mexico are considered to be the first civilization in America. • Mayans first appear on the Yucatan peninsula. • Very smart bunch… • Aztecs had an enormous empire throughout Mexico. • Large impact on modern Mexico. • http://www.history.com/videos/the-aztecs?cmpid=MRSS_Bing_HIS#the-aztecs
Hohokam and Anasazi • Hohokam • Irrigation Canals • Anasazi • Cliff dwellers– Mesa Verde, Chaco Canyon • Ditches and Basins
Hopewell and Mississippians • Hopewell • Created tools, clay pots. • Burial and Ceremonial Mounds • Mississippis • Great builders and architects
Question Time • What does it mean to be a “nomad”? • People who travel from place to place. • What does the Ice Age have anything to do American history? • Name two major Native American tribes the arose out of Mesoamerica. • Maya, Aztec
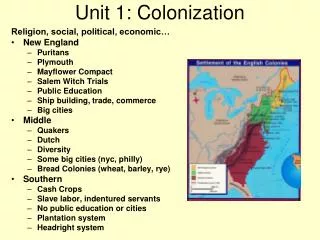
Native American Societies • Native Americans’ culture was effected by their environment. • Western Tribes • Far North Tribes • Eastern Woodland Tribes
The West • Southwest • Many small groups--Pueblo Tribes • Anasazi, Hohokam, Zuni, Hopi • Practiced corn farming, hunting, and gathering. • Pacific Coast • Many groups- Tlingit, Haida, Kwakuitls, Chinook, Salish • Harvested lumber, fished, hunted deer
The West • The Great Plains • Hopewell, Mississippian, Sioux, Pawnee, Kansas, Iowa • After the introduction of horses, they became great hunters and warriors. • Sioux famous for “scalping.”
The Far North • Inuit and Aleut • Depend on hunting whales, seals, and caribou. • Only Native American culture to develop lamps.
The Eastern Woodlands • Two distinct language groups – Algonquian, Iroquoian • Practiced slash-and-burn agriculture • Longhouses and wigwams • Iroquois often went to war with each other. • Founded the Iroquois League • Hiawatha - Chief
The Southeast • People of the Southeast were spread out and lived in towns. • Cherokee, Creek, Choctaw, Chickasaw, Natchez.
Sec. 3 - Africa • African culture is vital to American culture. • Islam – Most West Africans were Muslim. • Mosque – Islamic place of worship. • Trade routes between West Africa, Europe, and North America were impacted.
The Trade Game • Africa was important to North American colonization for two reasons. • 1. Gold, Sugar, and Spices Trade • 2. Slave Trade
Daily Objectives • Discover the causes of European exploration. • Why travel 5000 miles, experience hardship and possible death? • Were the Europeans technologically ready to explore?
Why this is important… • American society is most similar to European society for a number of reasons, but the main reason is that the United States was born out of Europe. • There had to be a reason/motivation for European exploration. We are going to discuss these reasons today!
The Crusades • 10th -14th Centuries • Crusades – Latin word crux, meaning “cross”. • Pope Urban II • Armed struggle against Arab Muslims. • – Regain the “Holy Land” • - Convert Muslims to Christianity • Importance • Influenced curiosity to travel and trade outside of Europe.
Fall of the Roman Empire • During the Middle Ages (500-1400), Europe experienced a decline after the fall of the Roman Empire. • Feudalism- Western European Kings grant power to nobles who owned land, creating an uneven heriarchy of power. • Manorialism – Economic ties between serfs and nobles • Created social classes
“I work very hard. I go out at dawn, driving the oxen to the field, and I yoke them to the plough; however hard the winter I dare not stay home for fear of my master; but, having yoked the oxen made the ploughshare and coulter fast to the plough, every day I have to plough a whole acre or more.” • --quoted in Colloquy
The Age of Discovery (15th -16th Centuries) • Back to the Crusades… • Demand for foreign goods was high in Europe (spices, sugar, salt, silk) • European traders reap huge profits • More tax $ for countries= more money spent on exploration. • Less reliance on the feudal system.
The Renaissance • Renaissance – 1350-1600 (about) • Intellectual revolution in Europe. • Highly influenced by the Middle East • New Technologies • Caravel (Portuguese), Lateen Sails (Indian) • Astrolabe (Muslim), Compass (Chinese)
New Technologies-cont. The Printing Press – 1454 – John Gutenberg • Greater access to maps and knowledge • Less “rediscovery”
Religion in Europe • 15th Century was rough for Roman Catholicism • Protestant Reformation • Indulgences • Martin Luther • Church of England
First European Explorers • Find a sea route to Asia • 1419 – Henry the Navigator • 1488 – Bartolomeu Dias • 1497 – Vasco da Gama • Discovered water route to Asia. • Vikings were first to the New World, about 1000 AD • Leif Ericsson – Set up colonies in Newfoundland, but they failed. No success, no credit!
Assessment • Look at the map on pg 34. First, answer question number 1. • Now, answer these questions: • After the discoveries of Bartolomeu Dias and Vasco da Gama, which European cities had the greatest trade advantages? • If I wanted to ship spices over land from India to Cordoba, Spain, what would be the easiest path for my goods to travel?
Sec. 5 Europe Encounters America
Question Time… • Why were Europeans ready to explore? • Why would they want to explore? • What happened that made them change their isolationist ways? • Make a cause and effect T-Chart justifying your response.
Cause and Effect of European Exploration Causes Effects Exchange of goods, services, and ideas between cultures. Slave Trade Disease swaps • Crusades • Weakening of Feudalism– More power for nobles, less for kings. • Renaissance • New tech.=> Compass, Astrolabe, Caravel • Competition between nations. • Missionary zeal - Pilgrims
Christopher Columbus • “America was discovered accidentally by a great seaman who was looking for something else: when it was discovered it was not wanted; and most of the exploration for the next fifty years was done in hope of getting through or around it. America was named after a man who discovered no part of the New World. History is like that, very chancy.” - Morison
Why is Columbus Famous?? • Leif Ericsson discovered North America nearly 500 years before Columbus. Why does history remember Columbus and not Ericsson? • History honors the successful…
Columbus Background • Christopher Columbus • Italian navigator, believed the Earth was round. • NOT a new idea. Claudius Ptolemy drew circular maps of the Earth in AD 200, complete with lines of longitude. Pg 39
Columbus’ Problem… • Columbus is quoted: “…the end of Spain and the beginning of India are not far apart… and it is known that this sea is navigable in a few days’ time with a favoring wind.” • Severely underestimated the size of the Earth. • Why important? –See Google Earth • Waited 7 years for final approval. • King Ferdinand of Spain
Columbus’ Voyage • Nina, Pinta, Santa Maria • Reached land Oct. 12, 1492 • Watlings Island, San Salvador (Bahamas) • Found very little… • Indengiounous People – Called them Indians • Small deposits of gold • Explores other islands, returns to Spain • Promises Ferdinand more gold than he can dream of.
Columbus • His findings encourage other expeditions. • His success is due to the fact that it was publicized.
Race to Claims • Portugal and Spain were nearly at war over disputing trade routes. Pope Alexander VI had a solution: • 1493- Line of Demarcation (Bull of Demarcation) • Vertical line of separation in the Atlantic ocean between Spain and Portugal. Spain gets the Americas. • 1494- Treaty of Tordesillas • Significance?
Spain Explores America • Juan Ponce de Leon – Governor of Puerto Rico, discovers Florida in 1513. Searched for the “fountain of youth”. • Vasco de Balboa – First European to reach Pacific coast of America.