3.Gate-Level Minimization
360 likes | 759 Vues
3.Gate-Level Minimization. Gate-Level Minimization – Two-Variable Map. xyz + xyz' = xy(z+z')=xy xyz + xy'z = x(y+y')z=xz xyz + x'yz = (x+x')yz=yz 인접항들의 결합임 xyz + x'y'z ‘ = ? (minimization 안됨 ) 즉 분배법칙을 통한 minimization 과정 인접항들을 찾는 과정 필요함 하나의 minterm 은 3 개의 인접항들을 갖음.

3.Gate-Level Minimization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
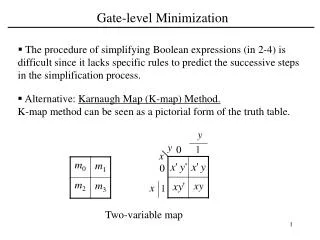
Gate-Level Minimization –Two-Variable Map • xyz + xyz' = xy(z+z')=xy • xyz + xy'z = x(y+y')z=xz • xyz + x'yz = (x+x')yz=yz 인접항들의 결합임 • xyz + x'y'z‘ = ? (minimization 안됨) • 즉 분배법칙을 통한 minimization 과정 인접항들을 찾는 과정 필요함 • 하나의 minterm 은 3개의 인접항들을 갖음
Gate-Level Minimization –Two-Variable Map • m1+m2+m3 = x'y +xy' +xy = x(y+y’) + y(x+x’) = x +y • Two-Variable Map • Three-Variable Map –위치 암기하기
Gate-Level Minimization –Three-Variable Map • Map 에서 인접셀은 변수중 하나만 complement 관계이고 나머지는 같은 변수로 이루어짐 • m0와 m4의 차이점? m0 + m4 = ? • m1와 m3의 차이점? m1 + m3= ? • m6와 m4의 차이점? m6 + m4= ? • m0 + m1 + m4 + m5= ?
Gate-Level Minimization –Three-Variable Map • Ex 3-1) Simplify the Boolean function, F(x, y, z) = Σ(2, 3, 4, 5) F = x'y + xy' • Ex 3-2) F(x, y, z) = Σ(3,4,6,7) F = yz+xz'
Gate-Level Minimization –Three-Variable Map • Ex 3-3) Simplify the Boolean function, F(x, y, z) = Σ(0,2,4,5,6) F = z'+xy' • Ex 3-4) Given Boolean function, F = A'C + A'B +AB'C +BC a) express it in sum of minterms F(A, B, C) = Σ(1, 2, 3, 5, 7) b) find the minimal sum of products F = C + A'B 위의 2개의 example 해볼 것
Gate-Level Minimization –Four-Variable Map Ex 3-5) Simplify the Boolean function, F(w, x, y, z) = Σ(0, 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 12, 13, 14) F = y'+ w'z' + xz' Ex 3-6) 해볼 것 1
Gate-Level Minimization –Prime Implicants • F(A,B,C,D) = Σ(0,2,3,5,7,8,9,10,11,13,15) F=BD+B'D'+CD+AD =BD+B'D'+CD+AB' =BD+B'D'+B'C+AD =BD+B'D'+B’C+AB'
Gate-Level Minimization –Five-Variable Map • Ex 3-7) Simplify the Boolean function, F(A,B,C,D,E)=Σ(0,2,4,6,9,13,21,23,25,29,31) F = A'B'E' + BD'E + ACE * 위의 예제 해볼 것
Product of Sums Simplification • Ex 3-8) Simplify the Boolean function, F(A, B, C, D) = Σ(0, 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, 10) a) sum of products F = B'D' + B'C' +A'C'D b) product of sum F = (A' +B')(C' +D')(B' +D)
Product of Sums Simplification • Ex 3-8) Simplify the Boolean function, F(A, B, C, D) = Σ(0, 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, 10) b) product of sum G=F' = AB + CD + BD' F = G'=(A' +B')(C' +D')(B' +D)
Product of Sums Simplification • F( x, y, z) = Σ(1, 3, 4, 6) = ∏(0, 2, 5, 7) F = x'z +xz' F' = xz +x'z' F = (x'+z')(x + z) * 위의 예제 해 볼 것
Don’t-Care Conditions x y F 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 x y F 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 x y F 0 0 1 0 1 X 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 X 0 1 F = x’y’ + xy F = x’ + y F = x’ + y
Don’t-Care Conditions x y F 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 x y F 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 x y F 0 0 1 0 1 X 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 X 1 0 F = y’ F = x’ + y’ F = y’
Don’t-Care Conditions • Ex 3-9) Simplify the Boolean function, F(w, x, y, z) = Σ(1,3,7,11,15) Don’t-care conditions, d(w, x, y, z) = Σ(0, 2, 5) F(w, x, y, z) = yz + w'x' = Σ(0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 11, 15) F(w, x, y, z) = yz + w'z = Σ(1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 15)
NAND and NOR Implementation • NAND 와 NOR 게이트가 회로적으로 구성 용이함 –어떠한 digital system 이라도 NAND 또는 NOR 로만 구성하는 것이 가능 • NAND Circuit (inverter는 하나의 입력이 ‘1’로 또는 2개의 입력이 하나로 결합된 형태의 NAND로 구현)
NAND and NOR Implementation (NAND : 2-level) • F = ((AB)'(CD)')' = AB + CD • Ex 3-10) Implement the following Boolean function with NAND gates: F(x, y, z) = Σ(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7) = xy' + x'y + z
NAND and NOR Implementation(NAND) • NAND 의 두가지 표현 방법은? • AND 와 OR 를 NAND 로 나타내시오.
NAND and NOR Implementation(NOR) • NOR Implementation (inverter는 하나의 입력이 ‘0’으로 또는 2개의 입력이 하나로 결합된 형태의 NOR로 구현) • F = (AB' + A'B)(C + D')
NAND and NOR Implementation(NOR) • NOR 의 두가지 표현 방법은? • AND 와 OR 를 NOR 으로 나타내시오. • F = (AB' + A'B)(C + D') 를 NOR 으로 나타내시오.
Wired Logic • Wired AND : Open collector • Wired OR : ECL
2-LEVEL • AND, OR, NAND, NOR 의 4개의 gate 고려 – 16개의 2 level 가능 • Degenerate form –하나의 동일한 gate 로 표현 가능. 즉 1 level 로 구현 가능 • AND-AND one AND AND-NAND one NAND • OR-OR one OR OR-NOR one NOR, • NAND-OR one NAND NAND-NOR one AND • NOR-AND one NOR NOR-NAND one OR • Nondegenerate form • AND-OR, OR-AND : standard form 으로 이미 학습 • NAND-NAND, NOR-NOR : 이미 학습 • NAND-AND, AND-NOR AND-OR-INVERT 로 구현 • OR-NAND, NOR-OR OR-AND-INVERT 로 구현 • Example 3-11(a)의 map 을 AND-OR-INVERT로 구현하고, 이를 각각 NAND-AND 및 AND-NOR로 그리시오.
Exclusive-OR Function • x y = xy' + x'y (만들어볼것) (x y)' = (xy' + x'y)' = xy + x'y' x 0=x x 1=x' x x=0 x x'=1 x y'=x' y=(x y)‘ • A B = B A (A B) C = A (B C) = A B C Fig. 3-32 회로가 EX-OR나오는지 풀어볼 것
Exclusive-OR Function • Parity Generation and Checking P = x y z (송신측) C = x y z P (수신측)
HDL(Hardware Description Language)(퀴즈 및 시험 안 나옴) • VHDL, Verilog HDL • Module Representation //HDL Example 3-1 //Description of the simple circuit of Fig. 3-37 module smpl_circuit(A,B,C,x,y); input A,B,C; output x,y; wire e; and g1(e,A,B); not g2(y, C); or g3(x,e,y); endmodule
HDL(Hardware Description Language) • 다음의 HDL의 내용으로 회로를 그리시오. module smpl_circuit(A,B,C,x,y); input A,B,C; output x,y; wire e; and g1(e,A,B); not g2(y, C); or g3(x,e,y); endmodule
HDL(Hardware Description Language) • Gate Delays - `timescale 1ns/100ps //HDL Example 3-2 //Description of circuit with delay module circuit_with_delay (A,B,C,x,y); input A,B,C; output x,y; wire e; and #(30) g1(e,A,B); or #(20) g3(x,e,y); not #(10) g2(y,C); endmodule
//HDL Example 3-3 //Stimulus for simple circuit module stimcrct; reg A,B,C; wire x,y; circuit_with_delay cwd(A,B,C,x,y); initial begin A = 1'b0; B = 1'b0; C = 1'b0; #100 A = 1'b1; B = 1'b1; C = 1'b1; #100 $finish; end Endmodule module circuit_with_delay (A,B,C,x,y); input A,B,C; output x,y; wire e; and #(30) g1(e,A,B); or #(20) g3(x,e,y); not #(10) g2(y,C); endmodule e
HDL(Hardware Description Language) • Boolean Expressions - AND, OR, NOT => (&), (|), (~) //HDL Example 3-4 // x=A+BC+B’D // y=B’C+BC’D’ //Circuit specified with Boolean equations module circuit_bln (x,y,A,B,C,D); input A,B,C,D; output x,y; assign x = A | (B & C) | (~B & C); assign y = (~B & C) | (B & ~C & ~D); endmodule
HDL(Hardware Description Language) //HDL Example 3-5 //User defined primitive(UDP) primitive crctp (x,A,B,C); output x; input A,B,C; //Truth table for x(A,B,C) = Minterms (0,2,4,6,7) table // A B C : x (Note that this is only a comment) 0 0 0 : 1; 0 0 1 : 0; 0 1 0 : 1; 0 1 1 : 0; 1 0 0 : 1; 1 0 1 : 0; 1 1 0 : 1; 1 1 1 : 1; endtable endprimitive • User-Defined Primitives (UDP) //Instantiate primitive module declare_crctp; reg x,y,z; wire w; crctp (w,x,y,z); endmodule