German Command Structure
490 likes | 807 Vues
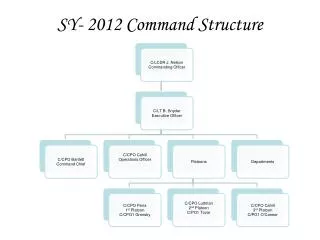
War Starts in Europe: German Command Structure Introduction to Tanks Blitzkrieg The Invasion of Poland. German Command Structure. OKW Oberkommando der Wehrmacht. OKL. OKM. OKH. Hermann Göring, 1893-1946. Franz Halder, 1884-1972. Erich Raeder, 1876-1960. Kurt Zeitzler

German Command Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
War Starts in Europe:German Command Structure Introduction to Tanks Blitzkrieg The Invasion of Poland
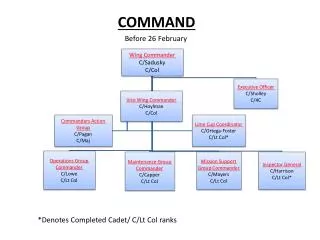
German Command Structure OKW Oberkommando der Wehrmacht OKL OKM OKH Hermann Göring, 1893-1946 Franz Halder, 1884-1972 Erich Raeder, 1876-1960
Kurt Zeitzler 1942-1944 d. 1963 Adolf Heusinger 1944 d. 1982 Heinz Guderian 1944-1945 d. 1954 Head of OKH “Chiefs of the German General Staff” Hans Krebs, April 45 d. 1945
Commanders-in-Chief of the German Navy Karl Dönitz, 1943-1945 d. 1980 Hans-Georg von Friedeburg, 1945 d. 1945 Erich Raeder 1928 – 1943 d. 1960
Commanders-in-Chief of the German Air Force Robert Ritter von Greim, 1945 d. 1945 Hermann Göring, 1935-1945 d. 1946
What is the tank’s mission? • Support the Infantry ? • an “infantry tank” • protection and firepower • A separate arm of the fighting force ? • speed and maneuverability
Considerations in tank design… • Mobility (reliability) • Firepower • Protection (weight)
The geography of a tank . . . • Hull • Tracks and road wheels • Turret • Main gun • Machine guns • Coaxial machine gun • Bow machine gun • TC’s machine gun
Larger guns More heavily armored PzK1 = 5.4 tons Tiger II = 70 tons US main gun evolution 37 mm 50 mm 75 mm 90 mm German guns 20 mm 37 mm 50 mm 75 mm 88 mm Tank evolution . . .
Relative armor thickness . . . 1945 • US M4 1.5 – 4.25 inches • German PzK5, “Panther” 1.6 – 4.3 inches • Soviet T-34/85 1.7 – 3.5 inches
Relative armor thickness . . . 1939 • PzK 1 .5 inches • PzK 2 .5 - 1.2 inches • PzK 3 1.2 inches
Death by tank . . . High Explosive
Death by tank . . . Kenetic Energy Projectile ( a big bullet )
The modern world . . . Kinetic Energy Round
XX XX
XX Airpower XX
XX XX
XX XX
1st Panzer Division 2nd Panzer Division 3rd Panzer Division 4th Panzer Division 5th Panzer Division 10th Panzer Division Panzer Division “Kempf” 2nd Light Division 3rd Light Division 4th Light Division Panzer Regiment 25 German Armored and Mechanized Units in Poland Out of 60 divisions.
16,000 troops 135-200 tanks
And then . . . • Norway • Change in the British Government • The Battle of France • The Battle of Britain