Chapter 19 Diffraction and Interference of Light
130 likes | 480 Vues
Chapter 19 Diffraction and Interference of Light. Objectives. 19.1 Relate the diffraction of light to its wave characteristics 19.1 Explain how light falling on two closely spaced slits produces and interference pattern and use measurements to calculate wavelengths of light

Chapter 19 Diffraction and Interference of Light
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Objectives • 19.1Relate the diffraction of light to its wave characteristics • 19.1 Explain how light falling on two closely spaced slits produces and interference pattern and use measurements to calculate wavelengths of light • 19.1 Apply geometrical models to explain single slit diffraction and two slit interference patterns
Objectives • 19.2Explain how diffraction gratings form interference patterns and how they are used in grating spectrometers • 19.2 Discuss how diffraction limits the ability of a lens to distinguish two closely spaced objects
Diffraction • Bending around an object. • Short Waves diffract less
Single Slit • Reminder: If the wave is too big, won’t fit through
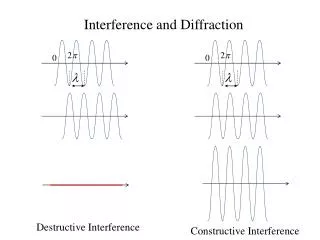
Vocabulary • Interference pattern: Produced by overlapping of waves (areas of dark and intense light) • Monochromatic: One wavelength of light • Coherent Waves: Wavelengths where crests and troughs line up exactly
Usefulness of Young’s Double Slit Experiment • How we were able to determine the wavelengths of light • We’ll avoid the math for now
Diffraction Grating • Lots of slits, able to produce patterns like the double slit
Diffraction Patters • Double Slit • Wavelength of light = X (Distance between interference bands on screen) D (distance between slits) / L (Distance from slits to screen)
Diffraction Patterns • Single Slit • Single Slit Equation: X = (Lamda)(L) / W (Width)
Astronomy Connection • Light from telescopes enters through a tiny opening which ends up diffracting the light just a bit. If two stars are too close, you may not be able to tell if there is one or two • The Rayleigh criterion for resolution