Diffraction and Interference
250 likes | 553 Vues
Diffraction and Interference. Physics Remember: Light is both a particle…and a wave. Light waves through an opening. The extent to which light waves bend depends on the size of the opening. Diffraction. Any bending of a wave by means other than reflection or refraction.

Diffraction and Interference
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Diffraction and Interference Physics Remember: Light is both a particle…and a wave
Light waves through an opening • The extent to which light waves bend depends on the size of the opening
Diffraction • Any bending of a wave by means other than reflection or refraction • Diffraction occurs when light waves pass through an opening. • Opening is large compared with the wavelength of the light • Light casts a sharp shadow with some fuzziness at its edges • Opening is extremely narrow • Because of diffraction, it casts a fuzzier shadow
The extent of diffraction depends on the relative size of the wavelength compared with the size of the obstruction that casts the shadow Waves tend to spread into the shadow region When the wavelength is about the size of the object, the shadow is soon filled in. c. When the wavelength is short compared with the width of the object, a sharper shadow is cast.
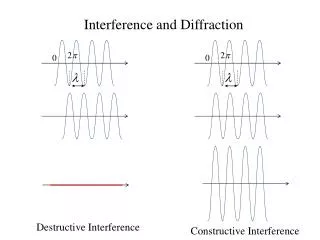
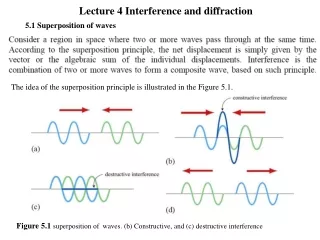
Interference • With an interference pattern, wave amplitudes may be: • increased, decreased, or neutralized • Recall: • Constructive interference • Destructive interference
Young’s Interference Exp • Monochromatic light—light of a single color—was directed through two closely spaced holes , and fringes of brightness and darkness were produced on a screen behind. • Bright fringes = constructive interference • Dark areas = destructive interference • Demonstrated the wave nature of light.
Light from O passes through slits A and B and produces an interference pattern in the screen
Thin film interference • The colors seen in thin films are produced by the interference in the films of light waves of mixed frequencies. • Ex: Soap bubble • Light that reflects from one surface may cancel light that reflects from the other surface • Ex: Gasoline on a wet street • Colors correspond to different thicknesses of thin film
The thin film of gasoline is just the right thickness that light reflected from the top surface of the gasoline is canceled by light of the same wavelength reflected from the water.
Incoherent Light • Light emitted by a lamp is incoherent • Waves of many frequencies and wavelengths that are out of phase • Light of a single frequency can still be out of phase
Coherent Light & Lasers • A beam of light that has the same frequency, phase, and direction is said to be coherent • No interference • Lasers produce coherent light LASER = Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation