Frictional forces
110 likes | 580 Vues
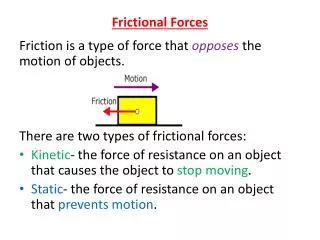
Frictional forces. Force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that are in contact with one another. Definition: . Cause. Irregularities on the surfaces that come into contact with one another. Dependent on. Types of surfaces that are in contact

Frictional forces
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Frictional forces Force that opposes the motion between two surfaces that are in contact with one another Definition:
Cause • Irregularities on the surfaces that come into contact with one another
Dependent on • Types of surfaces that are in contact • The forces that push the surfaces together
Static Friction • Force that opposes the start of motion • Use only when objects are not moving • When the magnitude of the force applied is greater than the magnitude of static friction, object moves
Kinetic Friction • The frictional force between two surfaces in relative motion • Less than the magnitude of static friction
How can we calculate friction? Ff = m x FN • m (mu) is the coefficient of friction • Takes into consideration the different types of surfaces • Table found on front page of Reference tables • Greater the value, greater the friction • FN is the normal force • Perpendicular to the surface objects rest on • Equal to weight (Fg) when object rests on a flat horizontal surface
Sample Problems A 10.0 kg wooden box sits at rest on a wooden floor. a. How many Newtons of force are needed to start the box moving? Ff = m FN Ff= (0.42)(98.1N) Ff= 41.2 N FN = Fg = mg Fg= (10.0 kg)(9.81m/s2) Fg= 98.1 N m = 10.0 kg m = 0.42
Once the box has begun to move, how many Newtons of force are needed to keep the box sliding at constant speed?