Scientific method
110 likes | 408 Vues
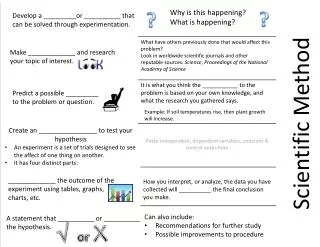
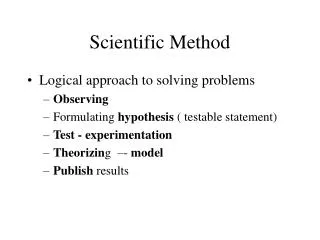
Alyssa Buckner 12-1-11 5 th hour. Scientific method. Observation. An observation is something you notice. The two kids are running, so your observation would be “kids.”. Research Question. A question is a question that can be tested.

Scientific method
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Alyssa Buckner 12-1-11 5th hour. Scientific method
Observation • An observation is something you notice. The two kids are running, so your observation would be “kids.”
Research Question • A question is a question that can be tested . Research question would be, “Do taller or shorter people run faster?”
Collecting Variables: IV, DV and CV • I.V.- something the experimenter changes • D.V.- changes because of what you changed • C.V.- stays the same Example: • I.V.- height of person • D.V.- speed that they run at. • C.V- person
Hypothesis • A hypothesis is an educated guessthat is in a “if” and “then” statement. Example: If we time both people running , then the person that is 5 feet tall will run faster then the person that’s 3 feet tall.
Procedure • Procedure is a step by step instructions on what you did to get your results. Example: Time a person that’s 3 feet tall running 5 yards Time a person that’s 5 feet tall running 5 yards Do 5 trials Find average speed for each person. Graph data
Analyze Data • After you find your data, you make T-Chart and a graph. • There are two types of graphs that you will use, line and bar graph • Line- when time is involved • Bar- when time isn't involved • To name the graphs it’s “the effect of” I.V “on“ D.V Examples: Persons height Speed The effect of persons height on their speed 3 Speed (minutes ) 3 feet 2 minutes 2 1 5 feet 3 5 1 minute Persons height (feet)
Bar and Line graph examples Bar Line
Conclusion • Saying if your hypothesis was correct or not. • So my hypothesis was,“If we time both people running , then the person that is 5 feet tall will run faster then the person that’s 3 feet tall.” After we tested it, the 5 foot person run faster then the 3 foot person. My hypothesis was correct. Example: My hypothesis was correct, the taller the person is, the faster they run