Disorders of Memory
401 likes | 2.08k Vues
Memory disorders encompass a range of conditions affecting the ability to encode, store, and retrieve information. Essential components include sensory memory, working memory, and long-term memory. Various types of amnesia—organic and psychogenic—can lead to memory impairment, such as inability to recall past events or learn new information. Distortions of memory may also arise, affecting recall accuracy. This guide explores the processes of memory, the impact of trauma, the phenomenon of false memories, and interventions to manage these disorders effectively.

Disorders of Memory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction • Memory: cognitive ability to encode, store, and retrieve information • What happens to information after it has been perceived is usually discussed under memory • Some information is forgottenalmost immediately whereas some might be retained for seconds, hours, years or even a lifetime Disorders of Memory
Basic Components of Memory • Sensory memory • Working memory (short term memory) • Long term memory Disorders of Memory
Three Stages Model of Memory Sensory Memory Encoding Attention Working Memory / STM Long Term Memory SI Retrieval Encoding Rehearsal Disorders of Memory
Remembering • Process of remembering • Registration • Retention • Retrieval • Recall • Most memory tests measure recall of prior events either from the persons life or from tests administered earlier Disorders of Memory
Remembering … • Autobiographical memory • Memories for events and issues related to oneself • Associated with the active experience of remembering • Flashbulb memories type of autobiographical memory which the person becomes aware of an emotionally arousing event Disorders of Memory
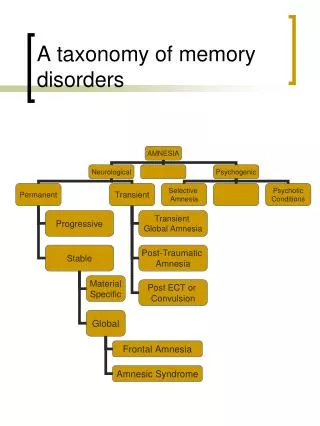
Memory Impairment • Amnesia • Loss of memory • Paramnesia • Distortions of memory • Hyperamnesia • Exaggerated of memory Disorders of Memory
Amnesia • Partial or total inability to recall past experiences and events • Origin may be organic or psychogenic • Failure to recall may also occur due to normal memory decay, i.e. unrehearsed items Disorders of Memory
Amnesia … • Interference from related materials • Proactive: old memories interfere with new learning hence with recall • Retroactive: new memories interfere with the retrieval of old materials Disorders of Memory
Organic Amnesias • Acute brain disease • Memory is poor owing to disorders of perception and attention hence failure to encode material in LTM • Acute head injury • Retrograde amnesia - events just before the injury • Anterograde amnesia - events occurring after the injury; common in accidents Disorders of Memory
Organic Amnesias … • Blackouts are circumscribed periods of anterograde amnesia • Experienced particularly by those who are alcohol dependent during and following bouts of drinking or acute confusion states (delirium) due to infections or epilepsy Disorders of Memory
Organic Amnesias … • Subacute coarse brain disease • Inability to register new memories or learn new information and inability to recall previously learned material • Memories from the remote past remain intact • Not diagnosed when there are other signs of cognitive impairment Disorders of Memory
Organic Amnesias … • Korsakoff’s syndrome • Thiamine deficiency or cerebrovascular disease, multiple sclerosis, transient global amnesia, head injury and electroconvulsive treatment – ECT • Chronic coarse brain disease • Loss of memory extending back into the recent past for a year or so • Ribot’s law of memory regression Disorders of Memory
Psychogenic Amnesias • Dissociative or hysterical amnesia • Sudden, occurs during periods of extreme trauma, can last for hours or days, commonly in prior head injury • Personal identity i.e. name, address, history; or events at the same time the ability to perform complex behaviors is maintained • Dissociation can be associated with a fugue or wandering state Disorders of Memory
Psychogenic Amnesias … • Katathymic amnesia or motivated forgetting • Inability to recall specific painful memories • Occur due to the defense mechanism of repression • Last for many years Disorders of Memory
Other Amnesias … • Anxiety amnesia • Occurs on anxious preoccupation or poor concentration in depressive illnesses or GAD • Depressive amnesia • Depressive pseudo dementia • Impaired concentration Disorders of Memory
Paramnesia • Distortion of recall and recognition • Occur in normal subjects due to • Process of normal forgetting • Proactive and retroactive interference from newly acquired material • People with emotional problems or organic states Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall • Retrospective falsification • Unintentional distortion of memory occurs when it is filtered through the person’s current emotional, experiential and cognitive states • i.e. description of past experiences in negative terms due to the impact of the current mood in depressive illness Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall … • False memory • Recollection of event(s) that did not occur but which an individual subsequently strongly believes did take place • Distortion of actual contraction of memories around events that never took place • Increased with age, worse in presence of organic brain disease Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall … • Screen memory • Recollection that is partially true and false • Only recalls part of the true memory because the entirely of the true memory is too painful to recall • Difficult to dissect out precisely which elements are objectively true in both therapeutic or legal settings Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall … • Confabulation • Occur in clear consciousness in association with organic pathology • Filling in of gaps in memory by imagined or untrue experiences that have no basis in facts • Embarrassed: person tries to fill in gaps as a result of awareness of a deficit • Fantastic: gaps are filled in by details exceeding the need of the memory impairment Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall … • Pseudologia fantastica or fluent plausible lying (pathological lying) • Confabulation that occurs in those without organic brain pathology i.e. antisocial personality disorder or hysterical type • Blurring of the boundary between fantasy and reality and when confronted with incontrovertible evidence they admit their lying Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall … • Munchausen’s syndrome • Variant of pathological lying in which a person presents to hospitals with bogus illnesses, complex medical histories and often multiple surgical scars • Proxy of it, a person i.e. parent produces a factious illness in somebody else generally their child • Long period of time for hospital services, diagnostic and management challenges Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall … • Vorbeireden or approximate answers • A person understand the questions but appear to be deliberately avoid the correct answer • Found in those consciously feigning illness (malingering), factitious disorder, or in acute schizophrenia Disorders of Memory
Distortion of Recall …. • Cryptamnesia • Experience of not remembering that one is remembering (Sims, 1997) • Not common neither associated with specific any specific psychiatry disorder • Retrospective delusions • Backdate delusions in spite of the clear evidence that the illness is of recent origin Disorders of Memory
Distortions of Recognition • Dejavu • Not strictly a disturbance of memory but a problem with familiarity of places and events • Comprises the feelings of having experienced a current event in the past, although it has no basis in fact • Jamaisvous • Knowledge that an event has been experienced before but is not presently associated with the appropriate feelings of familiarity Disorders of Memory
Distortions of Recognition … • Dejaentendu • Feeling of auditory recognition • Dejapense • New thought recognized as having previously occurred • Related to dejavu, different in modality of experience • Experience with normal people or with temporal lobe epilepsy Disorders of Memory
Distortions of Recognition … • False reconnaissance • False recognition or misidentification • Occur in organic psychoses, acute and chronic schizophrenia • In confusion states and acute schizophrenia at most a few people are positively misidentified, some in chronic schizophrenia can give false identity to every person they meet Disorders of Memory
Distortions of Recognition … • False reconnaissance … • In negative misidentification person insist that friends and relatives are not who m they say they are and that they are strangers in disguise • Some patients assert that some or all people are double of the real people whom they claim to be - Capgras syndrome • Occur in schizophrenia and dementia Disorders of Memory
Hyperamnesia • Exaggerated registration, retention and recall • Flashbulb memories associated with intension emotions, unusually vivid, detailed and long lasting • For example many people can recall where and what they were doing when heard sad news i.e. death • Flashback sudden intrusive memories that are associated with the cognitive and emotional experiences of a traumatic event • PTSD or substance misuse disorder, emotional events Disorders of Memory
References • Casey P, & Brendan K. (2007) Fish’s Clinical Psychopathology; Signs and Symptoms in Psychiatry 3rd Edition. The Royal College of Psychiatrists • Gross, R. (2010) Psychology the Science of Mind and Behaviors 6th edition; Macmillan Company • King, L.A (2008) the Science of Psychology, McGraw-Hill • Lahey, Benjamin. B (2004), Psychology an Introduction 8th Edition McGraw Hill Publisher Disorders of Memory