Patent Concep1
0 likes | 19 Vues
Startups and Intellectual Property Rights is the concept discussed in this article. Intellectual Property Rights are the Legal rights that are provided by the

Patent Concep1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Patent Concept: Startups and Intellectual Property Rights Startups and Intellectual Property Rights is the concept discussed in this article. Intellectual Property Rights are the Legal rights that are provided by the government agencies and the legal systems to an individual, or an organization including startups in the country where it is operating. These rights are drafted to encourage and reward creative activities by providing creators with exclusive control over their creations for a certain time. This blog will be a complete guide for registering a Startup under the Startup India Scheme. As startups lean on their fresh creative ideas and innovations, protecting them is the most crucial part. An Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) play a major role in doing so. These rights assist creators and inventors to protect their ideas and support further economic growth by giving them a means to profit from their work and investment in research and development. Role of Intellectual Property Rights in India Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) have a versatile role in India, embracing the protection of creativity, stimulating economic growth, supporting global trade, and balancing public interests. India has a robust legal framework for IPR, covering patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, and geographical indications. Copyrights provide protection for literary artistic, and musical creations, granting creators with reserved rights to their works. Patents galvanize innovation by affording inventors sole rights to their inventions, thereby propelling further research and development. Trademarks safeguard brand identity and reputation, nurturing consumer trust.
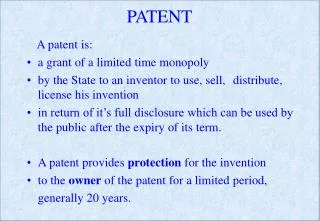
The economic impact of IPR in India is significant. They act as catalysts for economic growth by promoting investment in sectors that heavily rely on intellectual property, such as entertainment, technology and pharmaceuticals. They give businesses a competitive advantage, motivating them to invest in innovative ideas. Startups and Intellectual Property Rights: Startup India Scheme Startup India is a government initiative scheme introduced in 2016 with the aim of creating a favourable environment for startups to bloom. This brings us to Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), which are essential for startups and business. IPR refers to legal rights that protect the creation of the human mind, such as innovations, designs, literary and artistic works, and symbols, names, and images used in commerce. 1) Patents: These protect new inventions or processes for a certain period, granting the inventors exclusive rights to use, make, and sell the invention. 2) Trademarks: Trademarks secure the brand names, logos, and symbols, ensuring that consumers can identify and associate products or services with a specific business. 3) Copyrights: Copyrights protect original literary, artistic and creative works, such as books, music, and software. 4)Trade secrets: These are confidential business information and practices that provide a competitive advantage and are protected by non-disclosure agreements and other legal measures. Difficulties faced by Startups without Intellectual Property Rights Startups are like the engines of new ideas and business. They help make new things and improve the economy. But these small companies have a tough time protecting their creative ideas. Intellectual property rights are like the protection that keeps their ideas safe. Yet, many startups operate without adequate IPR protection, which exposes them to endless difficulties and risks.
1. Relentless Competition: One of the most immediate challenges for startups without IPR is the constant threat of competition. In the absence of protective patents or copyrights, competitors can easily copy the innovative solutions or products that a startup has worked tirelessly to develop. This not only weakens the startup’s uniqueness but can also lead to price wars and shrinking profit margins. 2. Valuation Dilemma: Investors play a crucial role in the growth of startups by providing essential capital and support. However, startups without strong IPR protection may find it difficult to attract investors. They don’t want to risk their money on something that might get copied easily. So, they might ask for more ownership in the company or give fewer good deals if they think the idea is not safe. 3. Talent Attraction and Retention: Creating a talented and passionate team is crucial for the success of a startup. However, the absence of intellectual property protection may dissuade skilled individuals from joining. Competent employees might be concerned about the possibility of competitors taking advantage of ideas developed while they are with the company. This can lead to difficulties in recruiting and retaining top talent, which can hinder the startup’s ability to effectively pursue its vision. 4. Scaling Challenges: Scaling a startup is a primary goal, but the lack of IPR protection can hinder this process. Startups must fight the possibility of copycat competitors entering the market, eroding their customer base, and potentially causing financial distress. Scaling a business needs substantial investments in marketing, infrastructure, and operations. 5. Limited Negotiating Power: In partnerships or licensing agreements, startups without IPR protection often find themselves at a disadvantage. Negotiating favourable terms can be challenging when the other party recognizes the startup’s vulnerability. This can lead to less advantageous deals, such as unfavourable revenue sharing arrangements or limited control over how the startup’s innovations are used.
Safeguard Intellectual Property using IPR for Startup Intellectual Property Rights are a set of legal protections and rights granted to individuals and entities for their intellectual creations. These creations encompass various categories including patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, industrial designs, trade dress, and geographical indications, each serving to protect different forms of intellectual property. These protections incentivize inventors, artists, and businesses to invest in research and development, artistic pursuits, and the creation of distinctive brands, as they can secure a competitive advantage and monetize their intellectual assets. Conclusion In conclusion, startups without Intellectual Property Rights face a multitude of difficulties. To mitigate these challenges, startups must consider the strategic use of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and non-disclosure agreements.