CASE 3
520 likes | 648 Vues
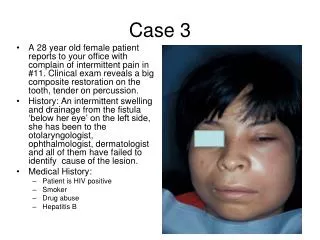
CASE 3. نرگس حجازی 5ساله با شرح حال تشنج فوکال که از 7روز قبل فنوباربیتال مصرف کرده است. Cc: تب از 2روز قبل و راش ماکولو پاپولر اریتماتوز T=39. LAB: WBC:7.1 3.7 HB: 11.9 12.2 PLT: 159 132 100 EOS: 3% 1% ESR: 15 35 CRP:3+ UC(-) BC(-)

CASE 3
E N D
Presentation Transcript
نرگس حجازی 5ساله با شرح حال تشنج فوکال که از 7روز قبل فنوباربیتال مصرف کرده است. Cc:تب از 2روز قبل و راش ماکولو پاپولر اریتماتوز T=39
LAB: WBC:7.1 3.7 HB: 11.9 12.2 PLT: 159 132 100 EOS: 3% 1% ESR: 15 35 CRP:3+ UC(-) BC(-) AST: 444 72 ALT: 394 227 ALP: 461
PLAN قطع فنوباربیتال و شروع کلونازپام قطع تب پس از 4روز بهبود راشها پس از 2روز
DX • DRESS S.
FOLLOW UP عدم ادامه تب WBC:6.9 HB:12.8 PLT:376 EOS:3.4 ESR”23 CRP:NEG ALT:14 AST:45 ALP:374
Case 4 • 5 month girl • Cc:FTT • History of 2 hospitalization for pneuminia and FTT • Bw:2700 • Nw:4.5
LAB: Wbc 16.4 ph:7.5 Hb:9 co2:29 Plt:318 Hco3:24.6 Ur:10 SE:NL Cr:0.3 AST:102 ALT54 ALP590 Na:134 K:3.4
CXR: infiltration Other lab NL PLAN: Ab therapy Sweat test: cl=65 na=55
DX • CYSTIC FIBROSIS • PLAN:SWEAT TEST
ID: AmirHosseinRahmani CC: Weakness PI: A 10yrs old male presented with nausea and headache from 1 days ago followed by walking disability and weakness. He had a history of paresthesia in distal parts of the limbs from 1 month later.
PMH Without a significant abnormality
Physical Examination Normal vital sign Normal general examination Normal cranial nerves Normal sensory system Normal DTR Force of lower limbs Flexor plantar reflex
Laboratory Data BS: 141 Urea: 36 Cr: 0.7 Na: 137 K: 4.5 Ca: 10.1 WBC: 11700 Neut: 80/ Lym: 12 RBC: 4.4 Hb: 12.6 Hct: 36.4 Plt: 323000 CPK: 248
EEG • Showed sharp waves at occipitotemboral lobe • Brain CT Scan: • Normal
Final diagnosis Conversion disorder
ID: SalehehGolmakani CC: Weakness and gait disorder PI: A 8 yrs old female presented with flue- like syndrome from 4 days ago followed by low back pain and walking disability.
PMH No significant abnormality
Physical Examination Normal vital sign Normal general examination Normal cranial nerves Sensory level at thoracolumbar area Decrease muscular force at lower limbs DTR of lower limbs Plantar reflex: Babinski
Laboratory Data • BS: 81 • Urea: 40 • Cr: 0.5 • K: 4.2 • Ca: 10.1 • Mg: 2.3 • U/A: Nl • RBC: 4.5/ Hb:13.5/ Hct: 39.4/ MCV: 85.8 • WBC: 7700 (neut: 72, lym: 20) • CSF: • sugar: 79/ pr: 19/ LDH: 26/ chol: 0 • WBC: 47 (neut:80, lym: 20)/ RBC: 0
others Anti- HIV: neg Anti- HTLV1: neg Anti ds DNA: 21 C3: 175 C4: 35 ANA: 9 RF: neg B/C: neg U/C: neg CSF/C: neg
SSEPS: • Nl • MRI: • hyperintensity of right temporoparietal lobe and medula at T2
Final diagnosis Demyelinating disorder probably MS
CASE 1 An 6 m old infant came with CC of FTT + Cough
Lab Results • VBG: Ph =7.30 • PCO2 = 13.7 • HCO3 = 7.7 • Urea : 19 _ Cr : 0.5 • U/A : Ph = 6 • U/C : Neg • B/C : Neg
Radiology • Plenty of stones with the size of 0.5 _ 1.5mm in calises in both kidneys and nephrocalcinosis
Diagnosis • Renal Tubular Acidosis type I (RTA I)
Diagnosis • Type I RTA is presented with normal AG(hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis) metabolic compensation for respiratory alkalosis produces an electrolyte pattern that is identical to that seen in a normal AG acidosis thus the first step in the diagnosis of the patient with the reduced serum bicarbonate and elevated chloride concentration is to confirm that metabolic acidosis is present by measuring the blood Ph
Urine Ph • Patient with normal renal function and normal renal acidification mechanism would develop metabolic acidosis usually have a urine Ph of 5.3 or less as ammonia (NH3) defuses into the tubular lumen it mostly combines with hydrogen ions to form ammonium (NH4+) the reduction in the free hydrogen ion concentration elevates the urine Ph depending upon the chronicity of the acidosis and the degree of hypokalemia the urine Ph may be 5.5 or higher .
In most cases of distal RTA the urine Ph is persistently 5.5 or higher
Treatment • The correction of the metabolic acidosis results is restoration of normal growth rates in children and also has the following benefits: • Minimizing new stone formation and nephrocalcinosis . • Demolishing calcium losses induced by bone buffering of some of the return acid .
The aim of alkali therapy is to achieve a relatively normal serum bicarbonate concentration (22 to 24 meq/lit) • Children may require as much as 4_8 meq/kg/day in divided doses because they often have a higher fix urine Ph as a result fixed bicarbonate losses are frequently higher than in adults . • Potassium citrate alone or with sodium citrate (polycitrate) is indicated in patient with persistent hypokalemia or calcium stone disease but not in patients with the hyperKalemic form of distal RTA
CASE 2 • A 3.5 year old boy with the history of 2 times complex seizure in the last month and under the treatment with Phenobarbital which happened to appear with fever , rash and conjuctivitis and didn’t respond to antibiotic therapy
Lab Results • WBC=4.1 3.9 3.4 9.5 3.8 • Hb = 9.1 10.5 9.1 9.2 8.1 • Plt = 128 191 434 690 544 • ESR = 12 70 101 • CRP = 3+ 2+ 3+
U/A : NL • U/C : Neg • B/C : Neg • AST = 131 41 • ALT = 134 65 • ALP = 649 • Echocardiography : NL