Exploring Planet Earth's Rock Cycle
240 likes | 359 Vues
Discover the fascinating journey of Earth's rocks over 4.6 billion years. From molten metal and rocks to the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, delve into the lithosphere and the rock cycle.

Exploring Planet Earth's Rock Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
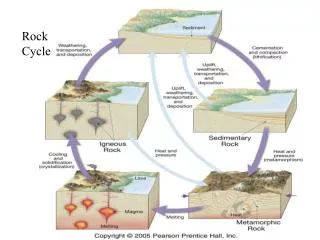
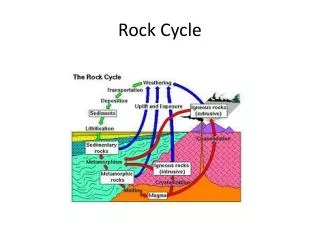
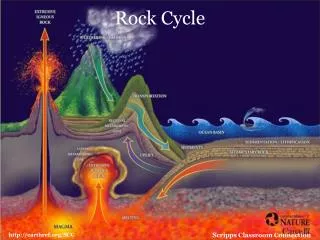
LITHOSPHERE ROCK CYCLE
Theage of PlanetEarth ... • Earth is about4,6 billionyearsold! • In the beginning Earthconsisted of moltenmetal and rocks. • Heavymetalssunkdeeper and lightermetalsfloatedatthe top.
Earth is ahugeball and consists of fourconcentriclayers Crust Mantle Outercore Inner core
THE CRUST • Thecrust of theearthlookssolid, butmovesconstantlyonthemoltenmantle. • Thecrust is dividedintohugeplates, thetectonicplates. • Thecrusts of thecontinentsconsistofgranite and quartz, whiletheoceaniccrustconsists of basalt. • Theoutermostlayer of themantle and thecrustformthelithosphere.
Tectonicplates https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1-HwPR_4mP4&feature=player_detailpage
Threemaintypes of rock • Igneousrock • Sedimentaryrock • Metamorphicrock
Igneousrock • FromGreek word meaning„fire”. • Moltenrock is called magma. • Whenmagma coolsdown and solidifies, igneousrockis formed. • Graniteformswhen magma coolsslowly and form big crystals. • Basalt and pumiceformwhen magma coolsfaster and formsmallcrystals. • Pumice also hasmanyholes – spacesfilledwith air/ bubbleswhenstill hot.
SEDIMENTARY ROCK – it is difficulttobelievethatthe Karoo was onceaninlandsea, untilyou see the koppies and layers of sedimantaryrock
Different types of sediment form different types of sedimentaryrock
Sedimentaryrock • Sedimentaryrockformswhenrockfragments and mineralparticlessettleatthebottom of thesea, alakeorariver. • Overtimethelayers of sand, silt and claybecomecementedtogetherunderhighpressure. • Sandstone, shale and limestone are examples of sedimentaryrock.
Metamorphicrock • Metamorphicrockformswhenigneousorsedimentaryrock are heatedor put underhighpressurefor a long time. • Marble and slate are metamorphicrocktypesthatcamefromsedimentaryrock put underheat and pressure.
Slaterock Slateroofing
Marble • Marble formswhenlimestone, asedimentaryrock, undergoesheat and pressure. • Themainmineral in marble (and limestone) is calciumcarbonate (CaCO3), givingitawhitecolour. • Thecolours of marble are duetootherminerals e.g. red marblecontainsironoxide.
White marblequarry in Tuscany Statue of Herakles