Rock Cycle
450 likes | 639 Vues
Rock Cycle. Just a Review. 3 Types of Rocks Igneous Sedimentary Metamorphic. Igneous Rocks. Formed by magma from the mantle cooling and becoming solid. Cooling may happen on the surface of earth. Form at volcanoes, plate boundaries, etc… E xtrusive igneous rocks.

Rock Cycle
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Just a Review • 3 Types of Rocks • Igneous • Sedimentary • Metamorphic
Igneous Rocks • Formed by magma from the mantle cooling and becoming solid. • Cooling may happen on the surface of earth. • Form at volcanoes, plate boundaries, etc… • Extrusive igneous rocks. • Cooling may happen below the crust. • Intrusive igneous rocks.
Categories – Crystal Size • Four types of igneous rocks • Course grained • You can see the crystals without a microscope. • Fine grained • You can only see the crystals with a microscope • Glassy • No crystals present • Porphyritic • Two sizes of crystals present
What Type of Igneous Rock??? Coarse Grained
What Type of Igneous Rock??? Fine Grained
Sedimentary Rock • Made of parts of other rocks that have broken into pieces. • Sediment = small parts of other rocks • Sediment made by weathering and erosion of igneous or metamorphic rocks. • Sediment often seen as layers in rocks. • Layers = strata • The formation of the sediment into one rock is called lithification.
Categories – Method of Formation • Clastic Sedimentary Rocks • Made from sediments that were transported to a new location by wind, rain, or animals. • Sediment can range is in size from large to very fine. • Regardless of size sediments lithified into one rock.
Categories – Method of Formation • Chemical Sedimentary Rocks • Formed when water evaporates and leaves behind a solid • Like when the water in salt water evaporates and leave behind salt crystals • Lithification happens when the water evaporates.
Metamorphic Rocks • Made from changing existing rocks into new rocks • Not like sedimentary…the rocks are not broken into pieces and reformed. They stay in one piece • Increasing the pressure or temperature or exposing them to a chemical will change the rock into a new type
2 Categories - Texture • Based on how the crystals align • Foliated (image b) • Non-foliated (image a)
2 Categories - Texture • Foliated Rocks • You can see distinct lines of different minerals. • They resemble pages in a book. • Non-Foliated • Sometimes you can see bent lines of different minerals. • Sometimes it just looks like a mixture of minerals with no order at all.
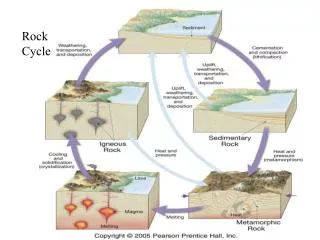
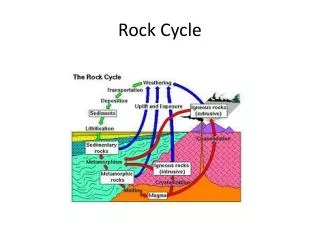
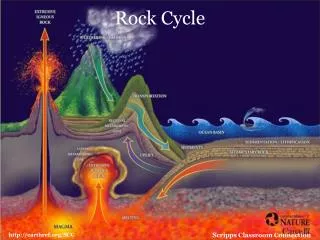
The Rock Cycle Magma
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools)
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Igneous Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Sediment
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Lithification Sediment
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Metamorphic Rock Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Melts Metamorphic Rock Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Melts Metamorphosis Metamorphic Rock Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Melts Melts Metamorphic Rock Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Melts Metamorphic Rock Igneous Rock Melts Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock
The Rock Cycle Magma Crystallizes (cools) Melts Metamorphic Rock Igneous Rock Weathering and Erosion Weathering and Erosion Metamorphosis Lithification Sediment Sedimentary Rock