1 / 0
Urbanization
0 likes | 200 Vues
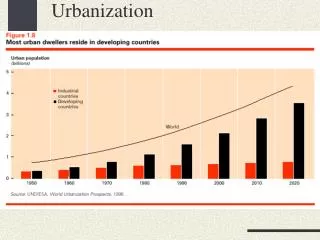
Urbanization. AP Human Geography Overview. Definitions. Urbanization – process by which people live and are employed in a city Nucleated Form of Settlement – center area of development (CORE AREA) Dispersed Form of Settlement – rural areas where houses are far apart
Télécharger la présentation 

Urbanization
An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation
Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author.
Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only.
Download presentation by click this link.
While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server.
During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
-
Urbanization
AP Human Geography Overview - Definitions Urbanization – process by which people live and are employed in a city Nucleated Form of Settlement – center area of development (CORE AREA) Dispersed Form of Settlement – rural areas where houses are far apart Thresholds – minimum number of people needed to meet the needs of an industry – amenities like pro sports teams
- History of Urbanization Early Cities – economic centers – small Medieval Cities – walls were constructed, church in center Indigenous Cities – constructed by natives before colonization Colonial Cities – after arrival of Europeans, major trading posts or ports Hydraulic Civilizations – government admin ensures water distribution to entire city
- Urban Economies Commercialization – selling of goods and services for profit Basic Industry – city forming industries (auto, steel, computers, etc) Nonbasic Industries – city serving industries include construction to industrial equipment Employment structure – industrial to tertiary/quaternary activities Post-Industrial City – specializing in information based work Deindustrialization – shift toward more specialized economic activities, factories shut down but new jobs appear in customer service, pro services, management Underemployment – too many employees are hired and there’s not enough work for them to do, layoffs ensue
- Urban Hierarchies Unincorporated areas – once considered urban, only 2-3 families live there today Hamlets – few dozen people, limited services Villages – larger than hamlets, offer more services Towns – 50-a few thousand, urban area w/ defined boundary, but smaller than city Hinterland – surrounding farms of the towns Cities – large, densely populated areas, 10s of thousands of people Metropolises – large population, large areas, focused around one city, over 50,000 people Megalopolis (conurbation) – several metro areas linked together to form one huge urban area
- City Types Emerging Cities – population growth, increasing economic and political clout throughout region Gateway Cities – connect two areas and serve as gateway Festival Landscape – space within an urban environment that can accommodate a large number of people
- Characteristics of US Cities Central Business District – commercial center – downtown Bid Rent Theory – only commercial landlords can afford the land w/in the central business district Shopping Mall – group of retail outlets that either share a roof or are connected by walkways Grid Street Systems – streets run east/west and north/south Suburbs – located on outskirts of central city, usually residential
- 4 Stages of US Cities Stage 1 – sail wagon period – 1790-1830, sailing (trade) Stage 2 – iron horse period – 1830-1870, railroad transportation Stage 3 – steel rail period – 1870-1920, steel building material Stage 4 – auto air amenity period – 1920-1960, engine (auto) transformed landscape
- European Cities Zoning Laws – determine how land and buildings can be used Residential Zoning – housing Commercial Zoning – business/retail Industrial Zoning – manufacturing plants Dendritic Pattern – root system of trees, streets curve and meander thru city Greenbelts – rural areas set aside to prevent development from extending too far outward In filling – process of cities that are close, merging together
- Latin American Cities Urban Growth Rate – rate at which individual cities increase their population Squatter Settlement – areas of squalor and extreme poverty (favelas and barriadas)
- Asian Cities Entrepots – reexport goods, sending them to all areas of the globe Office Parks – agglomerations w/ shared phone and internet services and transportation infrastructure High Tech Corridors – provide world w/ computer equipment needed to run its operations on a daily basis
- Islamic Cities Jani – primary mosque Bazaar – street market
- African Cities Colonial CBD – architecture resembles that of the colonizers’ country Traditional CBD – current commercial center of these cities Market/Bazaar CBD – sells anything and everything
- Models of US Cities Concentric Zone Model – lower classes live closest to the central business district while upper classes live farther out because they can afford the communte into city to work 1. Central Business District – peak land value 2. Zone of Transition – slums (high density areas of lower class citizens live in substandard housing, tenements – rundown apts) 3. Zone of Independent Workers’ Homes – lower class housing 4. Zone of Better Residences – middle class housing 5. Commuter’s Zone – upper class housing
- Models of US Cities Sector Model – based on class but describe social structure based on transportation systems rather than on distance from central business district 1. Central Business District 2. Transportation and Industry 3. Low Class Residential 4. Middle Class Residential 5. High Class Residential
- Models of US Cities Multiple Nuclei Model – urban growth is independent of the central business district, more emphasis placed on type of economic development 1. Central Business District 2. Wholesale, light manufacturing 3. Low Class residential 4. Medium class residential 5. high class residential 6. heavy manufacturing 7. outlying business district 8. residential suburb 9. industrial suburb
- Central Place Theory Shows relationship between urban areas (including hinterlands) and the range that individual cities need to maintain their size Range – max distance that people are willing to travel to purchase a product or partake in a service Threshold – product min number of customers needed for it to succeed Hinterland/market area – area in which a product, urban area, or commercial outlet has its influence Rank Size Rule – size of cities within a country will be in proportion to each other Primate city – more than twice the population of any other urban area in that country
- Built Environment and Social Space Catacombs – dead buried underground, pockmarks in the soil and ground unstable to support weight of skyscrapers Cityscape – artwork that shows a city Symbolic landscape – urban landscape that reflects a city’s history and has become synonymous with the city
- Suburbanization of the US Suburbanization – source of growth White flight – movement of white middle class people away from the inner city to the suburbs Underclass – people who are excluded from the creation of wealth Urban sprawl – second ring suburbs are growing infringing on surrounding rural areas Planned community – developer can plot out each house and can build the entire development from scratch
- Problems in Urban Areas Counterurbanization – problems become so great, people leave Decentralization – distribution of authority from central figure to other sectors in the city Centralization – opposite, focusing power into one authority Urban hydrology – how a city gets clean water to citizens and removes dirty water Urban heat island effect – cities create own heat by pollution and congestion Urban morphology – street patterns, structures, physical form of city Gentrification – process of wealthy people moving into inner city neighborhoods Post modern architecture – blends historical foundations with modern touches Modern architecture – boxy structures, concrete and glass Restrictive covenants – prevent economic decline of new gentrified areas Block busting – real estate agents try to induce people to sell homes because different race is moving into the neighborhood Racial steering – real estate agents show homes only in certain neighborhoods based on race of buyers Segregation – separation of races Redlining – refusal of lending institutions to give loans to minorities in high risk areas
More Related