Learning, Memory, Language
110 likes | 373 Vues
Learning, Memory, Language. 11/5/10. What is a memory?. An organism's ability to store, retain, and recall information and experiences. Memory Types. Declarative Memory. Working memory -Prefrontal Cortex. Semantic memory. Episodic memory. Storing Memory.

Learning, Memory, Language
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Learning, Memory, Language 11/5/10
What is a memory? • An organism's ability to store, retain, and recallinformation and experiences
Memory Types Declarative Memory Working memory -Prefrontal Cortex Semantic memory Episodic memory
Storing Memory • How do we go from “learning” to memory “storage”? • H.M.: • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBsW5qz5sDU
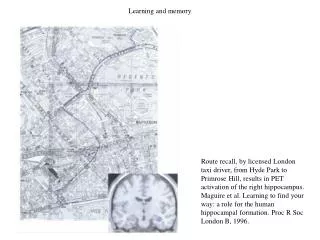
Storing Memory • Hippocampus and parahippocampal region play roles in converting short-term to long-term • Medial temporal region: forms/organizes/retrieves memories • Cortical regions: store long-term memories • A song to help you understand- • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Li5nMsXg1Lk
Retaining Memory • “Changes in synapses”… ? • Synaptic Plasticity- learning by adding or removing connections, or adding cells • LTP: Long-Term Potentiation • CHANGES in the synapse • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GMehTI6DPYI
Mechanism of LTP • Ca2+ enter synapse • Activation of cAMP • cAMP activates CREB (cAMP-response element binding protein) • CREB activates the production of neurotrophins: proteins that increase neuron sensitivity (decrease its threshold) I will Diagram on Board
Language • Left hemisphere = language master • Left frontal lobe: • Broca’s aphasia: trouble producing speech • Wernicke’s aphasia: trouble understanding speech • Word deafness: all possible speech problems combined into one disease
Language and Brain Areas • Speech recognition: L/R temporal lobes (anterior) • Speech production: L frontal lobe + L temporal lobe • Word meanings: stored in the L temporal lobe • Sensory/motor circuit for verbal short term memory: L posterior temporal lobe