Revision
150 likes | 366 Vues
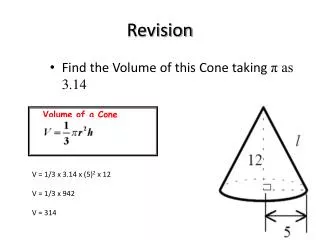
Revision. If an acid is added to a strong base, what happens to the base? What is neutralisation? What are the two products usually formed when acids and bases react? What do you get when you mix hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide? Why was the sherbet fizzy?. Acid rain.

Revision
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Revision • If an acid is added to a strong base, what happens to the base? • What is neutralisation? • What are the two products usually formed when acids and bases react? • What do you get when you mix hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide? • Why was the sherbet fizzy?
Acid rain 9 Sci: Acids and Bases
Acid Rain! Rain that is acidic… ‘Clean’ rain that is unpolluted normally has a pH of 5.7 • Why? • Carbon Dioxide and water mixes to form carbonic acid Acid rain contains other chemicals that lower the pH below 5.7
Natural Acid Rain Where would it be natural? Acid rain can occur naturally such as during volcano eruptions.
Acid Rain Cycle 2) In the presence of water, it gets converted into Sulfuric acid and nitric acid Nitric Acid Sulphur dioxide Sulphuric acid Nitric oxides 3) Acidic water damages environment and water 1) Burning of fossil fuels releases sulphur dioxide and nitric oxides
Effects of Acid rain Acid rain has been shown to have adverse impacts on forests, freshwater and soils. • Directly damaging forests, bushlands etc. • Killing animals, insects and aquatic life • Ruin soils for natural growth and plantations • Polluting waterways • Damaging buildings and monuments
Chemistry of Acid Rain The burning of fossil fuel releases Sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide: Sulphuric Acid SO2 SO3SO3 + H2O H2SO4 Nitric Acid NO2 + OH- HNO3 Sulphur dioxide Sulphur trioxide Sulphuric Acid Water Nitrogen dioxide Nitric Acid
Acid rain on biological life • Most fish will die and eggs won’t hatch below pH of 5. • Insects and molluscs cannot tolerate low pH (their shells get corroded) • Amphibians have sensitive skin • Plant leaves, branches and roots become damaged by the acid. • Low pH ruins the soil, plants can’t take up important nutrients for growth.