Multi-Junction Solar Cell
1.17k likes | 3.2k Vues
Multi-Junction Solar Cell. By Bryan Rogers. What is a Solar Cell?. A Solar Cell is a device used to trap light/photons and convert this to current Similar to a laser, it transmit light by physical properties and bandgap. http://www.solarsam.com/about-solar-energy/solarcells.html.

Multi-Junction Solar Cell
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Multi-Junction Solar Cell By Bryan Rogers
What is a Solar Cell? • A Solar Cell is a device used to trap light/photons and convert this to current • Similar to a laser, it transmit light by physical properties and bandgap http://www.solarsam.com/about-solar-energy/solarcells.html
Single vs Multi • Single-Junction Solar Cell • Multi –Junction Solar Cell http://home.howstuffworks.com/solar-light2.htm http://www.nrel.gov/continuum/spectrum/awards.cfm Advantages • A Single Solar Cell has an efficiency of about 34% while Multi-is above 43% • The leading cause to loss when converting light to current is the energy of the photon has • to be able to create a electron-hole pair. Multi-Junctions advantage is that it has multiple • band gaps that can be used to convert the light unlike single.
Bandgap • Electrons have to gain enough energy to overcome the bandgapof the material, and that energy is removed from the energy originally in the photon. • Stair stepping through the process, the photons travel through the multiple p-n junctions causing an increase in efficiency of gathering the energy http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multijunction_photovoltaic_cell
Properties • Wavelengths – Shortest wavelengths are on top, and ripple up as you pass through the Multi-Junction Solar Cell • Opposite for Bandgap, largest to smallest • Metallic Contacts – Made of aluminum • Anti-Relective Coating – this coating is used in several layers of the Multi Junction Cell. Its used for increasing the transmission coefficient. Without it the Solar Cell would lose about 70% efficiency • Tunnel Junctions – These junctions are designed to create minimal loss between two subcells. If this was not in place you would have P-N junctions in the opposite direction. They are created by highly doping the material to create a large bandgap.
Materials • Germanium for the bottom • GaAs for the middle - Gallium arsenide • GaInP2 for the top-cell - Indium phosphide • These 3 layers of choice are used because of how create their lattice matching is, the range of bandgaps used to convert light. They specifically target certain wavelengths/frequencies.
Loss & Efficiency • Blackbody Radiation- The Semiconductor are designed at certain temperatures and pressure that lead to loss because of operating levels • Recombination- When the electrons meet the holes left behind from previous excitations • Extraction of power is not fully converted from the photons • The photons have to make a electron-hole pair which does not always happen http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multijunction_photovoltaic_cell
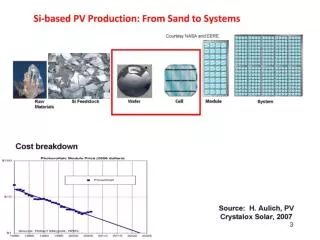
Growth • As materials become cheaper, this leads to increase research as the cost to create Multi-Junction Solar Cells which are not cheap. • Highest efficiency is ~44% these causes are only practical through concentrated light techniques. This technique takes advantage of sunlight area and condenses it down to focus on hitting the Multi-Junction Solar Cell. Can achieve upwards of 400 Suns, though if the sun is not direct the efficiency falls off dramatically. • If lattice matched perfectly and under the effects of concentrated Sunlight efficiency can get above 44%
Cost • The cost to create these Multi-Junction Solar Cells are very expensive hindering expansion and growth. • To create a very efficient MJ Solar Cell you have to be under concentrated light which is not practical, you have to have great lattice matching between materials. • Another problem is government subsidizing. In other countries around the world the government handles the cost allowing for research and unfair trading . In the U.S. this is problem because companies cannot compete with the prices to sell their goods.