Climate and Biodiversity
130 likes | 353 Vues
Climate and Biodiversity. Edward Aruna Founder/Managing Director Reptile and Amphibian Program – Sierra Leone edwardaruna@yahoo.com r eptile.amphibianprogram.sl@gmail.com. Introduction:- The Organization. Reptile and Amphibian Program – Sierra Leone (RAP-SL) was founded in Sept 2012

Climate and Biodiversity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Climate and Biodiversity Edward Aruna Founder/Managing Director Reptile and Amphibian Program – Sierra Leone edwardaruna@yahoo.com reptile.amphibianprogram.sl@gmail.com RAP-SL
Introduction:- The Organization • Reptile and Amphibian Program – Sierra Leone (RAP-SL) was founded in Sept 2012 • Against the background that herpes are somehow left out in most biodiversity assessment in Sierra Leone • RAP-SL hopes to document all reptile and amphibian species in Sierra Leone with sufficient evidences including photos, specimen, video clips etc. • Provide a center for information on reptiles and amphibians in Sierra Leone • Produce a field guide for future students and scientists wanting to take-up career in herpetology • Campaign for the protection of data deficient, threatened and endangered reptile and amphibian species and their habitats in Sierra Leone RAP-SL
Introduction • Undertake education/sensitization campaigns • Work with locals on community development issues in the form of compensation for behavior change. • Lobby government ministries for environmental/natural resources management laws’ implementation and enforcement RAP-SL
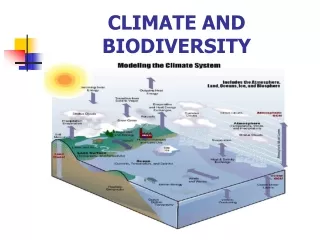
RAP-SL Roles and Responsibility in Climate and Biodiversity • RAP-SL acknowledges the following: • Climate is an important environmental influence on ecosystems. • Climate changes and the impacts of climate change affect ecosystems in a variety of ways. • For instance, warming/cold could force species to migrate to higher/lower latitudes or higher/lower elevations where temperatures are more conducive. • Similarly, as sea level rises, saltwater intrusion into a freshwater system may force some key species to relocate or die, thus removing predators or prey that were critical in the existing food chain. • Climate change not only affects ecosystems and species directly, it also interacts with other human stressors such as development. • For instance, climate change may exacerbate the stress that land development places on fragile coastal areas. • Additionally, recently logged forested areas may become vulnerable to erosion if climate change leads to increases in heavy rain storms. RAP-SL
RAP-SL Roles and Responsibility in Climate and Biodiversity • The following are likely results of CC • Changes in the Timing of Seasonal Life-Cycle Events • Range Shifts • Food Web Disruptions • Threshold Effects • Pathogens, Parasites, and Disease • Rarity and Extinction Risks RAP-SL
RAP-SL Roles and Responsibility in Climate and Biodiversity • Therefore, RAP-SL considers the following as important tools for CC and BD • Education and sensitization • Research and documenting changes over time • Campaigning for the protection of endangered, threatened and vulnerable species • Campaigning for the protection of vulnerable sites including coastal areas, islands, wetlands, savannah grasslands, forests edges etc. • Payment for behavior change RAP-SL
RAP-SL Involvement in Climate and Biodiversity • Education and sensitization • Research and documenting changes over time • Campaigning for the protection of endangered, threatened and vulnerable species • Campaigning for the protection of vulnerable sites including coastal areas, islands, wetlands, savannah grasslands, forests edges etc. • Paying for behavior change RAP-SL
RAP-SL Observation of Events and Trends • Over the years, it has been observed that we are loosing our forest covers and wetlands areas rapidly • Water supplies are alarming becoming scarce • Wildfire disasters in the north • Species rarity • Coastal erosions • Beach shifting • Sea water intrusion into freshwater • No clearly stated period for seasons in the country • Poor yield from farms • More grass and sandy lands RAP-SL
RAP-SL Recommendation • Prioritize adaptation efforts in communities where vulnerabilities are highest and where the need for safety and resilience is greatest. • Build projected climate change related trends in today’s risk and vulnerability assessment based on current climate variability. • Fully integrate adaptation into longer term national and local sustainable development and poverty reduction strategies. • Prioritize the strengthening of existing capacities – among local authorities, civil society organizations, and the private sector – to lay the foundations for the robust management of climate risk and the rapid scaling up of adaptation through community-based risk reduction and effective local governance. • Develop robust resource mobilization mechanisms for adaptation that ensure the flow of both financial and technical support to local actors. • Leverage the opportunities in disaster prevention and response, through improved early warning systems, contingency planning and integrated response, to promote effective community-based adaptation and risk reduction. RAP-SL
RAP-SL Recommendation • Education/sensitization campaigns • Vigilant land use plans • Protection of water sources/watershed areas • Enforcement of Laws • Creation of more protected areas (MPAs, Forest Reserves, National Parks, PAs • Carbon Credit projects • Sustainable utilization of resources RAP-SL