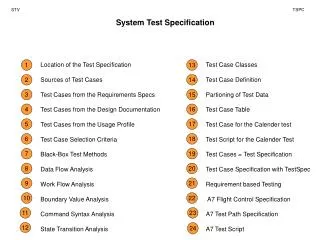
Disinfec tion a nd S terili sation MUDr. Lenka Černohorská, Ph.D
90 likes | 570 Vues
Disinfec tion a nd S terili sation MUDr. Lenka Černohorská, Ph.D. A seps is a nd antiseps is Aseps is : prevention against infec tion Antiseps is : p rocess of removing infec t i on. D e c ontamina tion met h od s. Rules of right de c ontamina tion. Right met h od or pr eparate :

Disinfec tion a nd S terili sation MUDr. Lenka Černohorská, Ph.D
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Disinfection andSterilisationMUDr. Lenka Černohorská, Ph.D • Asepsis and antisepsis • Asepsis:preventionagainst infection • Antisepsis: process of removing infection
Rules ofright decontamination • Right method or preparate: • Mustkillmicrorganisms • Can notdestroy desinfectedor sterilizatedmaterial • Should have: enough intensityof various factors (temperature, concentration…), enough time lenght
DISINFECTION PREPARATES • Peracetate acid (Persteril). For spores, funges and tuberculosis; 0,5% solution = highdegree desinfection! It’s agresive, unstabile, decolourize textile • Peroxid hydrogen (H2O2) - similar, less agresive, lesseffective – wounds washing. Halogen preparates: • chlornans:NaOCl -known as Savo,limychlor – forcesspools • Chloramin B – forhands, surfaces • Iod tincture (Jodonal B, Jodisol, Betadine), for wound desinfection.
Disinfection 2 • KMnO4– wound washing • Formaldehyd – for textil • Kresol (lysol) effective, but smell, agresive, not often used • Ethylalkohol – inmixture, not very effective; Highesteffectivityhas 70 % solution • Surface activepreparates - Ajatin - forskin desinfection, Septonex • Anorganicacids andalkaline • Hardmetals – for water reservoires etc. • Combinated preparates, for ex. Incidur
SterilizationI • Hotvapourunderpressure (autoclaves). Vapour must berightsaturated. Used forglass materials, metal, ceramic, pottery, porcelain, textil, rubber and some plastic materials. Temperature 121 – 134 °C. • Hotair sterilization (apparates with nucenou air circulation 180 °C 20 minutes or 170 °C 30 minutes or 160 °C hour). Usedfor metals, glass, porcelain andpottery. • Flowingsteam (Arnold apparatus) – sterilizationcultivationsoils
Sterilization II • Gama rays:used for glovesforone use. • Plasmatic sterilizationinhighfrequency electromagnetic field (modern method) • Chemical sterilizationvia formaldehyd steam or ethylenoxid. Used in case, where physical methods can’t be used. • Fireis used only for microbiological loops, damage other materials. Burnof rubbish. • Other methods: fractionate sterilization, filtration of solutionetc. - special methods, rare used
Before decontaminationisoften needed mechanicalwashing. • After decontamination:for ex.ventilate rest of chemical solution. Don’t letinstrumentsstay on table whole year etc.
Controlof disinfectioneffectivity andsterilization • Control of sterilization:chemical- indicators change their colourin specific temperature, biological- strains ofBacillusgenus absolveall cycle andafter that we discover if they alive. • After disinfectionwe do swabsfrom desinfectedsurface orletthe preparate influence tocontrol strains.