Exploring the Senses: Vision, Hearing, Smell, Taste, and Touch
100 likes | 213 Vues
Dive into the fascinating world of the senses - how we see, hear, smell, taste, and touch the world around us. Learn the intricate processes within our bodies that enable these sensory experiences. Discover the wonders of vision, hearing, smell, taste, and touch through this informative guide.

Exploring the Senses: Vision, Hearing, Smell, Taste, and Touch
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Vision • Light enters the eye through the cornea and is refracted • Passes through the lens and is refracted again • Light is directed unto the retina • Rods are sensitive to dim light • Cones are sensitive colors and bright light
Vision cont. • The image is then passed to the optic nerve • The optic nerve carries the image to the vision center of the cerebrum • The images is transmitted as upside down and reversed • The brain interprets an the image is viewed as the right side up • Both eyes work together and the brain blends the two images.
Lenses • Convex lenses- thicker in the middle • Concave lenses- thinner in the middle • Lenses are used to correct nearsightedness and farsightedness
Hearing • When an object vibrates it creates sound waves • These waves travel through solids, liquids, and gases • When they reach the ear they stimulate nerve cells deep within your ear and stimulate the auditory nerve which sends the sounds to the cerebrum.
The outer and middle ear • The outer ear intercepts the sounds and sends them down the ear canal to the middle ear. • The Eardrum in the middle ear vibrates moving through the anvil, hammer and stirrup. • The stirrup rests against a membrane in the inner ear.
The inner ear • The cochlea is a fluid filled shape in the inner ear that resembles a snail shell. • When the stirrup vibrates then fluids in the cochlea vibrate. • This causes an hair cells in the cochlea to bend and send electrical impulses to the cerebrum so you can hear.
Smell • When you smell something it is because it gives off molecules that the olfactory cells in your nose can detect. • If enough molecules are present then the olfactory cells will be stimulated to send a message to the cerebrum. • If you have encountered the smell before then your brain will remember it.
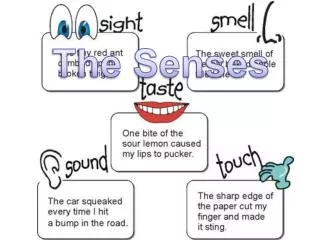
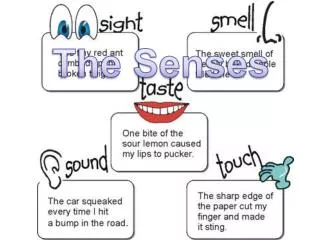
Taste • Taste buds are the sensory receptor cells for taste. • They are found on your tongue. • The major taste buds recognize sweet, bitter, salty, and sour. (also MSG)
Touch • Your internal organs have several kinds of sensory receptors- they respond to touch, pressure, pain, and temperature. • They send impulses to the brain and spinal cord. • Sensory receptors are located throughout the skin. • They can tell if an object is smooth, rough, hot, cold, hard and soft.