Accurate and Cost-Effective Indoor Location Estimation Using Kernel Methods
10 likes | 150 Vues
This paper discusses an innovative approach for indoor location estimation utilizing a mobile device in WiFi-covered environments. The challenge arises from similar signals not necessarily indicating proximity to the same locations. The proposed method maximizes the correlation between signal characteristics and actual locations through Kernel Canonical Correlation Analysis (KCCA). Experimental results showcase that the LE-KCCA approach significantly reduces calibration efforts, achieving an impressive accuracy with minimal samples compared to traditional methods, outperforming alternatives like SVM and MLE.

Accurate and Cost-Effective Indoor Location Estimation Using Kernel Methods
E N D
Presentation Transcript
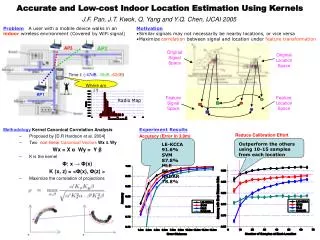
Original Signal Space Original Location Space AP3 AP2 Time t: (-47dB,-36dB,-62dB) Where am I ? Feature Signal Space Feature Location Space AP1 Accurate and Low-cost Indoor Location Estimation Using Kernels J.F. Pan, J.T. Kwok, Q. Yang and Y.Q. Chen, IJCAI 2005 Problem A user with a mobile device walks in an indoor wireless environment (Covered by WiFi signal) • Motivation • Similar signals may not necessarily be nearby locations, or vice versa • Maximize correlation between signal and location under feature transformation Accuracy (Error in 3.0m) Radio Map Methodology Kernel Canonical Correlation Analysis • Proposed by [D.R Hardoon et al. 2004] • Two non-linearCanonical Vectors Wx&Wy Wx = X α Wy = Y β • K is the kernel Φ: x → Φ(x) K (x, z) = <Φ(x), Φ(z) > • Maximize the correlation of projections Experiment Results Reduce Calibration Effort • LE-KCCA 91.6% • SVM 87.8% • MLE 86.1% • RADAR 78.8% Outperform the others using 10-15 samples from each location