Network Analyzer Error Models and Calibration Methods by Doug Rytting
930 likes | 1.66k Vues
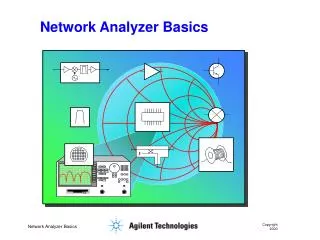
Network Analyzer Error Models and Calibration Methods by Doug Rytting. Presentation Outline. Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model System Error Model for Error-Correction One-Port Error Model and Calibration Two-Port Error Models and Calibration 12-Term Method

Network Analyzer Error Models and Calibration Methods by Doug Rytting
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Network Analyzer Error Models and Calibration Methods by Doug Rytting
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
8-Term to 12-Term: Forward 12-term model if add 2 crosstalk terms
8-Term to 12-Term: Reverse 12-term model if add 2 crosstalk terms
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Presentation Outline • Network Analyzer Block Diagram and Error Model • System Error Model for Error-Correction • One-Port Error Model and Calibration • Two-Port Error Models and Calibration • 12-Term Method • 16-Term Method • 8-Term Method • 8-Term Examples • Measuring S-parameters • E-Cal • Accuracy of Error-Correction
Electronic Calibration Standards Dave Blackham & Ken Wong
Electronic Calibration Standards are Transfer Standards Definition: Devices that derived their characteristics from measured data relative to primary or physical standards or other transfer standards. Dave Blackham & Ken Wong
First Generation Solid State Electronic Calibrator Transmission Line PIN Diodes Dave Blackham & Ken Wong
Second Generation Solid State Electronic Calibrator Discrete FET Switches PORT B PORT A Dave Blackham & Ken Wong