Petroleum and Tars Sands
120 likes | 299 Vues
Petroleum and Tars Sands. By Cameron Aenlle-Rocha & Chris Parker. What are Tar Sands?. Combination of clay, sand, water, and bitumen , a heavy black thick oil. Tar sands are mined Tar Sands does not come in a liquid form in its natural state

Petroleum and Tars Sands
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Petroleum and Tars Sands By Cameron Aenlle-Rocha & Chris Parker
What are Tar Sands? • Combination of clay, sand, water, and bitumen, a heavy black thick oil. • Tar sands are mined • Tar Sands does not come in a liquid form in its natural state • Tar Sands are processed to extract the oil-rich bitumen, which is then refined into oil.
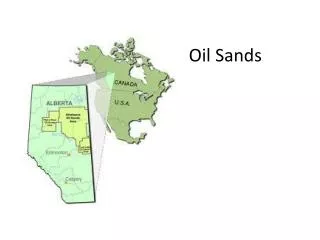
Tar Sands Resourcefulness • Much of the worlds oil is found in tar sands • Tar sands recently classified as part of the world’s oil reserves • Not all of that oil is recoverable • Largest deposit of Tar Sands is found in Canada and Venezuela • 20% of US crude oil and products come from Canadian tar sands
Tar Sands Resourcefulness • The United States is starting to explore Tar Sands as an alternative to conventional oil • The making of liquid fuel from tar sands requires energy for steam injection and refining • Process generates 12% more greenhouse gasses per barrel that the production of conventional oil
Advantages and Disadvantages • Relatively new form of energy • World has yet to really explore this option in forms of mass energy production • Water, sand, waste, and minerals must be removed from tar sands • Not very effective refinement process • Refinement
Petroleum to Gasoline • Extracted from the ground • Refinery • Shipped around the country via pipelines • Pump System
Demand for Petroleum • 35.1% of Total Energy demand • 19.1 Million barrels of oil a year • 50% more oil needed now that in 1973 (1st crisis) • Petroleum replaces coal (WWII) • Import half of crude oil
More Numbers • 2.22% Heating Oil • 4.45% Heavy Fuel Oil • 4.44% Liquefied pet. Gases • 9% Jet Fuel • 15% Other products • 22% Diesel • 42% Gasoline
Use for Petroleum • Gasoline, Fertilizers, Plastics, even Medicine • Fuels cars, jets and other modes of transportation
Advantages • Living the way we have been in the recent past • State and Federal lawes strickly regulate petroleum in an attempt to minimize negative effects
Disadvantages • Pollution (Air and Water) • Wildlife Habitat Damage (Water and Land)
Work Cited • http://www.treehugger.com/fossil-fuels/canadas-tar-sands-so-destructive-it-makes-its-well-paid-workers-want-quit-video.html • http://ostseis.anl.gov/guide/tarsands/index.cfm • http://www.need.org/needpdf/infobook_activities/SecInfo/PetroS.pdf