Pre-Test
230 likes | 413 Vues
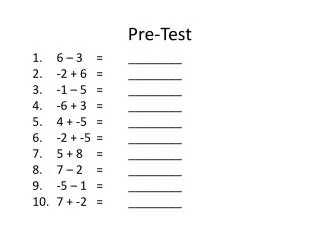
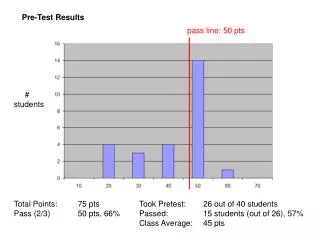
Pre-Test. 6 – 3 = ________ -2 + 6 = ________ -1 – 5 = ________ -6 + 3 = ________ 4 + -5 = ________ -2 + -5 = ________ 5 + 8 = ________ 7 – 2 = ________ -5 – 1 = ________ 7 + -2 = ________. Learning Theory. What is 25 X 25 ?. What is 25 X 25 ?. Types of Learning.

Pre-Test
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pre-Test 6 – 3 = ________ -2 + 6 = ________ -1 – 5 = ________ -6 + 3 = ________ 4 + -5 = ________ -2 + -5 = ________ 5 + 8 = ________ 7 – 2 = ________ -5 – 1 = ________ 7 + -2 = ________
Types of Learning • Problem solving (Rules) • Facts • Physical skills
Problem Solving • The behavior • The rule statement
Problem SolvingAdding Integers • The behavior-7 + 5 • The rule statementwhen the signs are different, subtract and use the sign of the larger number
Types of Learning • Tying your shoes • Solving: 5X + 3 = 2X – 7 • Spelling hippopotamus • Swinging a bat • knitting Name some other skills that are problem solving Name some other skills that are facts Name some other shills that are physical
Learning Learning is an internal process under the control of the individual Teaching is an external process under the control of the instructor
Students • Listen • Study • Practice
Teachers • Teachers set the (external prompts for the) CONDITIONS OF LEARNING
Conditions of Learning • For each type of learning, there should be different types of conditions
Conditions (Steps) in LearningProblem Solving (Original Learning) • Discriminate between items • Classify items into groups • Name the groups • Determine a solution strategy (an algorithm) • If possible, give the behavior a rule statement
Algorithm • A step by step procedure to solve a problem
Discriminate Between Items • X2 + 3X = 6 • 3X – 8 = 2X + 5 • 3X2 = 9 • 3X + 6 = 2X • 9X = 18X2 • X = 0 • 9X + X2 = 0 • How do you solve Algebra I problems? • How do you solve Algebra 2 problems?
A General ApproachTo Solve Problems (After Original Learning) • Recognize the problem • Remember the algorithm
Recognize the problemRemember the algorithm a • 8 – 3 = ________ • -3 + 5 = ________ • -4 – 9 = ________ • -4 + 5 = ________ • 8 + -5 = ________ • -3 + -6 = ________ • 5 + 4 = ________ • 3 – 2 = ________ • -6 – 2 = ________ • 9 + -5 = ________
Summary Types of learning Problem solving the behavior the rule statement Facts Physical skills Steps in learning (Original learning – learning for the first time) Discriminate between items Classify items into groups Name the groups Approach to Problem Solving (After original learning) Recognize the problem Remember the algorithm
Name the Command Structures • Tree Commands • Fluid User Interface (FUI)
Classify into Groups
Name the Groups • Group 1 • Group 2 • Group 3