The Lipids
560 likes | 758 Vues
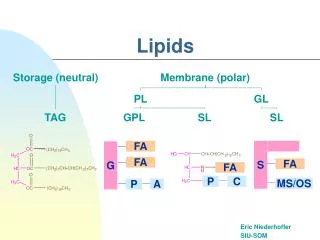
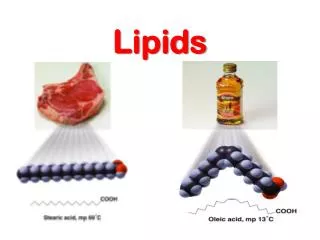
The Lipids. Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols. Lipids. Triglycerides (TG) Fats and oils Phospholipids Sterols. glycerol-a sugar alcohol, backbone of a FA! REM: they have carbon (C), so they are organic!. Fatty Acids (FA) & TG. FA & TG. glycerol + 3 FA TG + H 2 O.

The Lipids
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Lipids Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols
Lipids • Triglycerides (TG) • Fats and oils • Phospholipids • Sterols
glycerol-a sugar alcohol, backbone of a FA! REM: they have carbon (C), so they are organic! Fatty Acids (FA) & TG
FA & TG glycerol + 3 FA TG + H2O
Condensation of Glycerol & Fatty Acids to Form a Triglyceride
Fatty Acids • Length (size matters) • Saturated vs. unsaturated • Acetic Acid (most simple)
Saturated Fatty Acids • How many carbons? Stearic acid – 18-carbon Simplified structure
Fatty Acids • Point of saturation (where?) • Degree of saturation (how much?) • Saturated fatty acid • Monounsaturated • Polyunsaturated
An impossible chemical structure: Why? Oleic acid – 18-carbon, monounsaturated Linoleic acid – 18-carbon, polyunsaturated
TG: Why Does Saturation Matter? • Unsaturation effects: • Firmness • Stability • Oxidation • Antioxidants
Triglycerides:Whatabout “hydrogenated oils?” • Hydrogenation-hydrogen added to mono- or polyunsaturated fats to make them solid by reducing the number of double bonds (C=C). • Cis vs. trans-fatty acids
Cis- and Trans-Fatty Acids Compared So what? It’s a nice picture.
Trans fats are bad!!! • In the body trans fats behave like saturated fats! Why? • They contribute to higher LDL cholesterol and lower levels of "good" HDL cholesterol = heart disease.
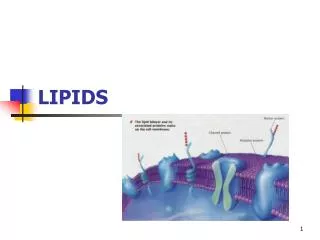
Phospholipids (PL) • Phospholipids in foods • Roles of PL • Plasma membrane • Emulsifiers (help oil and water exist together)
Membrane Structure PL Hydrophobic tail vs. hydrophilic head: more on this later.
Sterols • Roles of sterols: Good • Bile acids • Sex hormones • Adrenal hormones • Vitamin D • Roles of sterols: Bad -Atherosclerosis-hardening of arteries.
Fat Digestion Yummy...or not.
Fat Digestion • Hydrolysis • Triglycerides monoglycerides, fatty acids, glycerol
Fat Digestion • Mouth • Melting • Lingual lipase
Fat Digestion • Stomach • Churning and mixing • Gastric lipase
Fat Digestion • Small intestine • CCK-hormone which signals bile release! • Bile emulsifies fats.
Fat Digestion • Small intestine • Pancreatic lipases • Intestinal lipases
Enterohepatic circulation Note how fiber helps remove excess cholesterol!! Fat Digestion
Lipoproteins and health Factors that lower LDL and raise HDL • Weight control • Replace saturated fat with monounsaturated fat and polyunsaturated fat in the diet • Soluble fibers • Phytochemicals • Moderate alcohol consumption • Physical activity (biggest helper) • Genes influence lipoprotein activity.
Roles of Triglycerides • Fat stores • Energy • Protection • Insulation
Storage as fat Adipose tissue LPL = lipoprotein lipase...fat storage.
Lipid Metabolism • Using fat for energy • Hormone-sensitive lipase...triglyceride release. • Provides very little glucose...problem during fasting?
Health Effects of Lipids • Blood lipid profile • Heart disease • Risks from saturated fats
Health Effects of Lipids • Benefits:monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats • Cancer • Obesity
Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of Lipids • Recommended Intakes of Fat • DRI: 20-35% of energy intake (400-700 kcalories of a 2,000-kcal diet). • FDA recommends 10% of energy intake from s • Linoleic acid AI Linolenic acid AI 5-10% of energy intake 0.6-1.2% of energy intake • aturated, 30% of energy intake total fat
Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of Lipids • Daily Values • 65 g fat based on 30% of 2000-kcal diet • 20 g sat. fat based on 10% of 2000-kcal diet • 300 mg cholesterol • USDA Food Guide considers saturated fats discretionary kcalories. • Too little fat can be detrimental to health.
Health Effects and Recommended Intakes of Lipids • Health Effects of Lipids • Blood lipid profile • Reveals concentrations of lipids in the blood • Desirable levels • Total cholesterol < 200 mg/dL • LDL cholesterol < 100 mg/dL • HDL cholesterol ≥ 60 mg/dL • Triglycerides < 150 mg/dL
Guidelines to Groceries • Milk and milk products • Vegetables, fruits, and grains • Invisible fat