Solutions to group problems
180 likes | 319 Vues
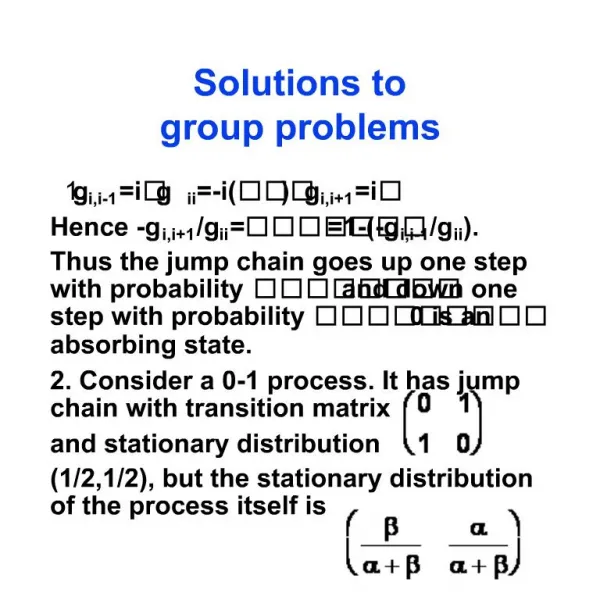
This text discusses the characteristics of jump chains in stochastic processes, focusing on their transition probabilities. It explores the relationships between the states in the chain, emphasizing the concepts of absorbing states and stationary distributions. An example of a 0-1 process with a transition matrix that has a stationary distribution of (1/2, 1/2) is considered, highlighting the importance of understanding these systems in probability theory and statistical mechanics.

Solutions to group problems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
1. Solutions to group problems gi,i-1=i? gii=-i(???) gi,i+1=i? Hence -gi,i+1/gii=???????=1-(-gi,i-1/gii). Thus the jump chain goes up one step with probability ????????and down one step with probability ?????????0 is an absorbing state. 2. Consider a 0-1 process. It has jump chain with transition matrix and stationary distribution (1/2,1/2), but the stationary distribution of the process itself is