Plate Tectonics
130 likes | 310 Vues
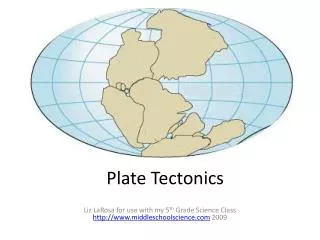
Plate Tectonics. 9 .1 Continental Drift. Evidence for Continental Drift Pangaea Alfred Wegener – proposed continental drift as a theory Continental Drift – continents have moved slowly to their current locations Pangaea – one large landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago.

Plate Tectonics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift
Evidence for Continental Drift • Pangaea • Alfred Wegener – proposed continental drift as a theory • Continental Drift – continents have moved slowly to their current locations • Pangaea – one large landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago. • Pangaea means “all land” • Continental drift was accepted long after Wegener’s death in 1930. • Fossil Clues • Mesosaurus found on both Africa and South America. • Glossopteris found on Africa, Australia, India, South America, and Antarctica.
Climate Clues • Warm weather plants were found on Spitzbergen in the Artic Ocean. • Wegner hypothesized that Spitzbegen drifted from the tropic regions. • Glacial clues • South America, Africa, India, and Australia were onece covered in glaciers • Rock Clues • Rock make up of the continents should be the same. • Similar rock sturctures are found on different continents. • Appalachian Moutnains in US are similar to Greenland and western Europe
How could continents drift? • Although there was evidence, Wegener couldn’t explain how or why continental drift happened. • Continental drift was rejected. • After Wegner’s death, more clues were found. • Seafloor spreading helped explain how continental drift could occur. Pg 251 1-3
Plate Tectonics 9.2 Seafloor Spreading
Clues on the Ocean Floor • Little was known before 1950s • Has mountains and valleys • mid-ocean ridges form an underwater mountain range that stretches along the center
The Seafloor Moves • Seafloor spreading • Hot les-dense material below Earth’s curst is forced upward toward the surface • Turns and flows sideways carrying the seafloor away • As seafloor spreads apart, magma moves upward and flows from the cracks • Becomes solid as it cools and forms a new seafloor • The seafloor cools, contracts, and becomes more dense. • Colder seafloor sinks down • Age Evidence • Glomar Challenger – drilling rig that allowed scientists to drill into the seafloor to obtain rock samples • Seafloor rocks are no older than 180 million years • Youngest rocks are at the mid-ocean ridges
Magnetic Clues • Earth’s magnetic field has a north and a south pole • Magnetic lines leave Earth near the north pole and enter near the south pole • Magnetic reversal – magnetic forces run the opposite way • Earth’s magnetic field has reversed many times • Iron-bearing minerals show the reversal of magnetic field • Magnetic reversals form parallel strips to the mid-ocean ridges
Plate Tectonics 9.3 Plate Tectonics
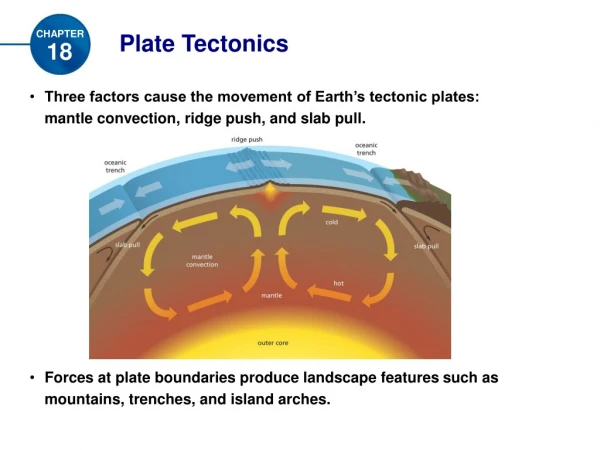
Plate Tectonics • Plate Movements • 1969s – combined continental drift and seafloor spreading. • Plate tectonics – Earth’s crust and upper mantle are in sections that move. • Plates – the sections of the Earth’s crust and upper mantle • Composition of Earth’s Plates • Lithosphere – crust and part of the upper mantle • Asthenosphere – plastic like layer below the lithosphere • Plates of the lithosphere “float” on the asthenosphere
Plate Boundaries • Plates Moving Apart • Divergent boundary • Seafloor spreading • North American pate is moving away from the Eurasian and African plates – Mid-Atlantic Ridge • Great Rift Valley in eastern Africa • Plates Moving Together • Convergent boundary • 3 types • Subduction zone – oceanic plate forced under a continental plates and volcanoes form • Two seafloor plates collide, one sinks, new magma forms island arc of volcanoes • Two continental plates collide, forming mountain ranges. Earthquakes are common
Plates Sliding Past Each Other • Transform boundaries • Two plates slide past one another, either in the same directions at different rates or opposite directions • Pacific plate and North American plate form San Andreas Fault