break
380 likes | 784 Vues
2: Population genetics. break. Problem of small population size. Small populations are less fit (more vulnerable) than large populations. In small populations drift is dominant. Small N -> Large G -> low genetic diversity.

break
E N D
Presentation Transcript
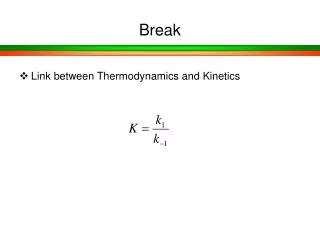
2: Population genetics break
Problem of small population size Small populations are less fit (more vulnerable) than large populations
In small populations drift is dominant. Small N -> Large G -> low genetic diversity. In small populations each individual has higher chances to be homozygous for deleterious genes. This is the same problem as in inbreeding. Notably, small populations do not harbor more deleterious genes, they just have more homozygotes for these genes
Population size and drift-selection balance Selection helps fixing “good” alleles (alleles that are positively selected). In small populations drift can be a stronger evolutionary force than selection and good alleles may disappear.
Conclusion Population size and the level of genetic diversity of a population are good indicators of the health of a population.
Example Panthera pardus nimr
2: Population genetics break
Effective population size It was noted that lab populations of drosophila tend to loose their genetic diversity faster than expected by genetic drift models. The reason is that in a population not all individual reproduce. In other words, the number of individuals do not always reflects the number of individuals that contribute their alleles to the next generation.
Effective population size The effective size of a population (Ne) is the size of an ideal population that has the same properties with respect to genetic drift as our actual population.
Examples when Ne and N differ • When the number of individual vary through the time • generation 1 = 10,000 individuals • generation 2 = 10,000 individuals • generation 3 = 100 individuals (bottleneck) • generation 4 = 10,000 individuals • generation 5 = 10,000 individuals
Bottleneck b b B B B b b B b B b b b b B b b b b b b b b
Bottleneck Population bottlenecks occur when a population size is reduced for at least one generation. Because genetic drift acts more quickly in small populations, undergoing a bottleneck can substantially reduce the genetic variation of a population and change the frequencies of alleles, even if the bottleneck does not last for very many generations.
Bottleneck • When the number of individual vary through the time • generation 1 = 10,000 individuals • generation 2 = 10,000 individuals • generation 3 = 100 individuals (bottleneck) • generation 4 = 10,000 individuals • generation 5 = 10,000 individuals The effective size of the population is closer to 100 individuals than to 1,000.
Founder effect The loss of genetic variation when a new colony is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population
Derivation of Ne when population size varies When size varies
Derivation of Ne when population size varies Approximations
Derivation of Ne when population size varies N is big, 1/N2 is small…
Derivation of Ne when population size varies An ideal population with size Ne will behave similar to a population that varies in size according to the above equation in terms of H’.
Examples when Ne and N differ When the number of breeding male Nm and breeding female Nf differ. In lions Nm< Nf
Lion group structure Lions are the only 'social' cats, whereby related female lions live together and form groups called 'prides'. Lion prides are family groups with all of the females related, mothers and daughters, sisters and cousins, etc, While female lions will live with the pride for life, male lions will only last two to four years before they are evicted or killed by a new coalition of male lions that take over the pride.
Drift and sex ratio: the formula Ne is the effective population size Nf is the number of females Nm is the number of males (without proof)
Example A population of 100 individuals, consisting of 10 breeding males and 90 breeding females , would lose genetic variability as rapidly as a population consisting of only 18 males and 18 females or 36 individuals
2: Population genetics break
Conservation Biology • Which species to protect? • (species that lost a lot of diversity or more variable species) • Where to place natural reserves? • (should we consider areas that have a lot of species, or areas that have genetically different individuals) • What should be the size of reserves? • (a too small reserve will not protect against drift)
2: Population genetics break
Example of founder effect [Huchon et al. 1999 Molecular Ecology 8, 1743–1748]
Armadillo founder effect Dasypus novemcinctus (nine banded armadillo)
Armadillo founder effect • The expansion of the range of the nine-banded armadillo into the USA is unique among placental mammals in that it has been occurring since the mid-19th century at a mean rate of 10 km a year. • This fast migration may have resulted from a low predation on adults, a lack of natural competitors, a weak homing ability (although it is rather sedentary with small home ranges), and human-induced translocations.
Armadillo founder effect • The researchers compared the genetic diversity of the North-America armadillo population to that of French Guiana
Haplotype • They compared the number of haplotypes = combinations of one or more alleles (e.g., in a sequence, each unique set of SNPs is considered an haplotype). • They sequenced the mitochondrial control region (which is relatively highly variable).
USA armadillo are significantly less diversed than those of French Guiana outgroup 2 haplotypes greatest distance between two captured armadillos was 1,026 km 10 haplotypes greatest distance between two captured armadillos was 32 km
2: Population genetics break
Speciation and geographical distribution • Populations that are at the limit of the species range tend to be slightly different from the rest of the populations. • New species have higher chances to appear from these populations.
2: Population genetics break