Understanding Mass Balance and Transport Mechanisms in Thermodynamic Systems
180 likes | 292 Vues
This article explores the principles of mass balance and mass flow in thermodynamic systems, including both diffusion and convection processes. We discuss the equations governing mass transport through permeable membranes, equilibrium conditions, and how alterations in pressure and temperature affect species activity. The concepts of momentum and energy balance are also highlighted, illustrating their significance in natural phenomena and engineered systems. This comprehensive overview helps grasp the underlying dynamics of mass transport and equilibrium in various phases.

Understanding Mass Balance and Transport Mechanisms in Thermodynamic Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
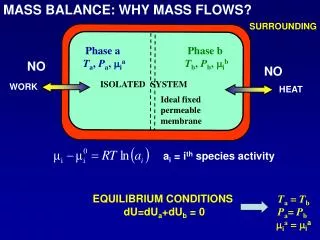
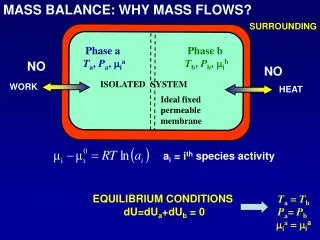
MASS BALANCE: WHY MASS FLOWS? SURROUNDING Phase a Ta, Pa, mia Phase b Tb, Pb, mib NO NO ISOLATED SYSTEM WORK HEAT Ideal fixed permeable membrane ai = ith species activity Ta = TbPa= Pb mia = mia EQUILIBRIUM CONDITIONS dU=dUa+dUb = 0
MASS BALANCE: EQ.CON. ALTERATION 1 Pa increase (>Pb) [Ta = Tb; mia = mib] Phase a T, Pa, mi Phase b T, Pb, mi MASS TRASPORT (CONVECTION) permeable membrane
mia>mib [Ta = Tb; Pa = Pb] 2 Phase a T, P, mia Phase b T, P, mib permeable membrane MASS TRASPORT (DIFFUSION) Mass transport represents a possible way the system has to get new equilibrium conditions once the original ones have been altered.
MASS BALANCE Z X Y DZ DX (X+DX, Y+ DY, Z+ DZ) G (X, Y, Z) DY (X, Y+ DY, Z) (X+DX, Y+ DY, Z)
MASS BALANCE: EXPRESSION DX DZ (X, Y, Z) G DY Ci = f(X, Y, Z, t)
DX DZ (X, Y, Z) G DY DIVIDING FOR DV
FLUXES EXPRESSIONS Ideal solution Diffusion Diffusion Diffusion Convection Convection Convection Bi = mobility of the diffusing components
MASS BALANCE EQUATION FOR ith SPECIES where: Remembering the definition of the NABLA operator:
As: … the summation of ith mass balance over all the r components yields to the well known continuity equation:
MASS BALANCE: CYLINDRICAL COORDINATES Jir+dr Jir+dr Jiz Jiz+dz Jir Jir Jir Jiz Jiz+dz Jir+dr r dr dz TWO DIMENSIONS r z
Ci = f(z, r, t) r dr dz Dividing by 2prdrdz
Constant diffusion coefficient D Remembering the derivativedefinition
MOMENTUM BALANCE Incoming sand Escaping sand Sand containing vessel Sliding vessel motion direction Inclinate plane Friction Gravity NO Yes
DZ DX (X+DX, Y+ DY, Z+ DZ) (X, Y, Z) DY (X, Y+ DY, Z) (X+DX, Y+ DY, Z) Body forces: gravitational, electro-magnetic fields Surface forces: viscous drag and pressure
Surface forces gravitational field Incoming and exiting mass
ENERGY BALANCE Conduction Expansion Viscous heating