Mutation
160 likes | 643 Vues
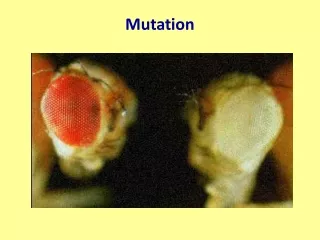
Mutation. Bellwork. Explain the role of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in translation. Objectives. Define mutation Explain the difference between base substitution and frameshift mutation Explain how mutations affect living things. Key Terminology. Mutation Base substitution Point mutation

Mutation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bellwork • Explain the role of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in translation.
Objectives • Define mutation • Explain the difference between base substitution and frameshift mutation • Explain how mutations affect living things
Key Terminology • Mutation • Base substitution • Point mutation • Frameshift mutation
Definition • Any change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA • Can result from • Single base change • Large regions of the chromosome change
Mutations within a gene fall into two general categories • First category- • Base substitution – replacement of one nucleotide with another • aka point mutation Ex. Normal gene AUG AAG UUU GGC GCA Met Lys Phe Gly Ala Mutated Gene AUG AAG UUU AGC GCA Met Lys Phe Ser Ala
Second Category • Frameshift mutation • adding or deleting a base can alter the reading frame (triplet groupings) • the codons downstream from insertion/deletion will be regrouped into different codons Ex: Normal Gene AUG AAG UUU GGC GCA Met Lys Phe Gly Ala Base Deletion AUG AAG UUGGCG CAU Met Lys Leu Ala His
Think-Pair-Share Explain the difference between base substitution and frameshift mutation? 3 PROPERTY OF PIMA COUNTY JTED, 2010
Mutagenesis • Process by which mutants are created • Can occur in two ways • Spontaneous mutation • result from errors during DNA replication or recombination • Exposure to a physical or chemical mutagen • Physical • exposure to x-rays and/or ultraviolet light • Chemical • Chemicals that interfere with correct DNA replication • They insert themselves and distort the double helix causing errors
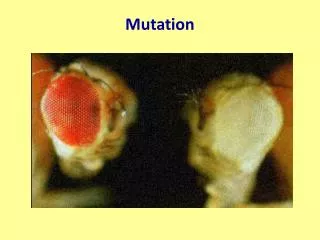
Effect of Mutations • No effect • mutations can be neutral • have little or no effect on protein structure or function • Harmful • mutations that produce defective proteins that disrupt normal biological activity • Beneficial • alter protein structure or function that enables to adapt better to their environment
Think-Pair-Share “Mutation is the driving force of evolution”. Explain that statement 3 PROPERTY OF PIMA COUNTY JTED, 2010
20 Word Summary 48 37 18 21 14 13 23 In 20 words or less, summarize the most important aspects from today's lesson. 12 PROPERTY OF PIMA COUNTY JTED, 2010