Organization Design and Management
350 likes | 666 Vues
Organization Design and Management. Edward F. Crooks MD, CMQ, CLSSBB. Organization Design and Management. The field of organization design and management considers how and why people behave as they do in organized setting.

Organization Design and Management
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Organization Design and Management Edward F. Crooks MD, CMQ, CLSSBB
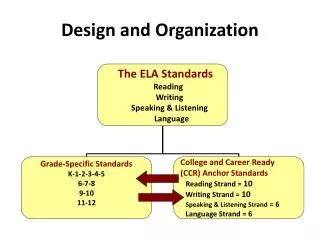
Organization Design and Management The field of organization design and management considers how and why people behave as they do in organized setting. The key to a successful organization is to have continuous and dedicated study of human behavior and attitudes, management systems, and organized structures that produce high quality medical and health care organization. The challenge for leaders in charge of quality is to design organizational structure and management systems that lead to transparent assessment of current state of quality, continuous effort to improve quality and ongoing monitoring of quality of care.
Organization Design and Management Effective leaders should • Be competent in the perception, motivation, and empowerment of individuals as well as group dynamics, characteristics of high-performance teams, and intergroup collaboration strategies. • Know how the diverse elements of organization design contribute to HQO. • Incentives • Reinforcement strategies • Strategic planning • Development and maintenance of culture and values • Psychological aspects of open access to information and data feedback
Organization Design and Management Traditional QA • Individual responsibility of a professional • Maintained autonomy • Administrative and professional authority over quality • QA teams established goals through planning • Driven by responses to complain • Failure to maintain goals was indicated by retrospective performance reviews. TQM • Offers a collective, management led, team oriented approach. • The whole organization QM is proactive and internally driven, seeking the best clinical and administrative structure.
Organization Design and Management System Thinking System is a set of two or more elements that satisfy the following: • The behavior of each element has an effect on the behavior of the whole. • The behavior of the elements and their effects on the whole are interdependent. • Regardless of how the subgroups of the elements are formed, each has an effect on the behavior on a whole and none has an independent effect on it.
Organization Design and Management Sociotechnical View of Quality Improvement • Quality derives from addressing the whole jobs, not part of jobs. • Workers must have autonomy to improve quality. • Authority for quality improvement must be delegated. • Group rewards must support team-based quality improvement. • Barriers to quality improvement must be eliminated. • QI evolves by recognizing the value of people. • Innovation for improvement supports quality. • Quality is driven by internal and external factors. Adapted from: Pasmore WA. Designing Effective Organizations: The Sociotechnical Systems Perspective. New York: Wiley; 1988
Organization Design and Management An organization is viewed as a whole, guided by values and principles, interacting subsystems, and structure and processes of integration. Every system is though to comprise of subsystems including • Product and Technical • Structural • Psychosocial • Managerial • Organization
Organization Design and Management Product and Technical System • Core work of the HCO • Varies based on the activities of the organization as a whole and of its subunits. • Shaped by production and delivery process, specialization of knowledge and skills required and of equipment involved and layout of the facilities. Structural • Involves the ways in which the task of the organization are divided and coordinated. • Organization charts, position and job descriptions, and rule and procedures define the structure.
Organization Design and Management • Basis for establishing formal relationships between clinical process and worker psychology. • Financial incentives are a structural tool that can be used to enhance the quality of clinical performance.
Organization Design and Management Psychosocial • It is the psychosocial dynamics of individual and groups that interact. • Varies from organization to organization. • Forces outside the internal structure help to establish the organization’s psychological climate within which physician, administrators and staff perform their clinical and administrative roles and activities. • This subsystem elements include individual behavior and motivation, status and rule relationships, and group dynamics as well as value, attitude, expectations, and aspirations of the people in the organization.
Organization Design and Management Managerial • Coordinates and the integrates the product and technical, structural, psychosocial and cultural subsystems • It relates the organization to its environment. • Set the goals • Develops comprehensive strategic and operational plans • Designs the structure • Establishes evaluation and control processes.
Organization Design and Management • Managerial activities includes • Planning • Organizing • Developing • Directing • Leading • Controlling • Curriculum development • Training • Performed through a series • of managerial roles: • Interpersonal • Informational • Decisional
Organization Design and Management Organizational Culture • Links the goals and the values of the members of the organization with those of the broader society. • This includes the concept of corporate culture and the ability to understand culture as part of clinical and administrative problem solving. Each of the subsystem is part of the architecture that must be created to stimulate quality improvement. • Each subsystem contains barriers (internal forces) • Inadequate clinical knowledge • Poor teamwork • Resistant leadership
Organization Design and Management • There are also external supra forces outside the boundaries of the organization: • Economics (e.g. state and natural economy) • Politics ( e.g. cost containment, policy incentives) • Technology ( e.g. new equipment, pharmaceuticals) • Social and demographics (e.g. single family, aging, crime) • Law (e.g. malpractice) • Culture (e.g. expectation, alternative medicine) • Natural resources (e.g. water, weather) • Globalization (e.g. war, pollution)
Organization Design and Management Responsibilities of a Leader of Quality Improvement Five responsibilities are essential: • Advocacy and Spokesmanship • MQ leader takes the lead in articulating and stimulating discussion of quality values with clinical and administrative staff. • Policy Planning, and Visioning • Expectation of the quality leader is present the competitive advantages of quality and to lead the development of the organization’s formal policies on QM • Should be represented in strategic discussion and should be equal in prominence to other strategy such as cost reduction, profit margins and market share.
Organization Design and Management • Delivery System Decision Support • Leaders in QI must be able to relate to many levels of authority, and bridge gaps in culture and perception. • Leaders in QI must play an integral role in the redesign and reengineering efforts to achieve overall clinical and business quality and safety. This includes greater internal integration of department and more sophisticated information system. • Analysis and Control of Quality • QL is responsible for the identification and collection quality data, conducting the required analyses and acting on the result to stimulate continuous improvement of the delivery system. • External Liaison and Representation
Organization Design and Management CEO Symbolic QL Establishes a culture with quality values and continuous improvement philosophy MQL fully represent these values in practice, helping the organization to meet and exceed professional and accreditation standards Purchasers Regulators Consumers
Organization Design and Management Quality Leaders: • Content Experts • Guide the institution to a clear and effective system based on state-of-art quality philosophy and methods. • Educators • Teaching clinical and administrative staff about primary and advanced knowledge and skills that have developed in the quality field. • Process Experts • Use of interpersonal communication and group skills to lead management and personnel through the development and usage of a system of quality management. • Evaluators • Constantly assessing the state of their QMS and searching for ways to improve its design and operations.
Organization Design and Management Successful performance in these roles requires that QLs have the authority and power to influence behavior- to create concerted, coordinated efforts to deliver and constantly improve quality.
Organization Design and Management Double Track (Strategic Formulation and Implementation) • Strategic decisions affect quality. • Leaders of quality must have a voice in the direction of the enterprise (strategy) and in execution of the strategies (operations). • This requires leaders in QI to attack problems and opportunities in two dimension.
Organization Design and Management Double Track (Strategic Formulation and Implementation) • Track 1 – is at the organization level – leaders make a public and a strategic commitment to improve quality • This requires executive leaders to promote the strategic importance of redesign and to create a vision of an improved quality future. • Track 2 – project or team level • Involves very specific and operational problems
Organization Design and Management Process for Track 2 • Problem identification • Team formation • Diagnosis of the problem • What do we do • Crafting solutions • Implementation
Organization Design and Management The double track approach is based on several common purposes: • Evaluation and assessment • Teaching and learning • Organizational change and development
Organization Design and Management One of the key responsibility of leaders of quality is to enhance efficiency and effectiveness of High-Performing teams (HPT) HPT has the following characteristics: • Size and structure • 8 to 15 members • Shared Vision • Have a clear goal and how the committee’s work fits into the institution’s objectives • Focused objectives • Near-term projects are clearly defined. • Members have chosen objectives that are manageable within a time frame, resources are available and a defined purpose that is limited in scope. • Leadership • Requires informed, participative leadership that is determined to receive input from all members. • Leader domination or loss of control undercuts enthusiasm and commitment • If attention is pay to team management, overtime the power of the team will add significant value to the task.
Organization Design and Management • Cohesion • Members of a HPT are in harmony with the task and have a concern for other members’ values and position • Action • Documentation of team activities with forward movement is key to maintaining members interest • Follow-up • HPT pay attention to 2 questions: • What effect did our action have? • What has been our year-long contributions to the organization’s performance
Organization Design and Management Hoshin Planning Strategic planning is linked to Hoshin Planning. Although there are some differences, they are quite close. Hoshin is intended to: • Linked strategic planning (high-level, long term) with operational planning and implementation (front-line, short term) ensuring that the best vision and intentions are realized. • The elements of Hoshin are directed at making this two-pronged effort meld into one organization-wide, smoothly integrated behavior.
Organization Design and Management Essential elements of Hoshin Methods: • QI effort is intended to be inclusive of staff at all levels. • The leadership of the organization must buy into and visible support the planning process. • Resources are substantial, and are used to support significant training at the start, with coaching and advisory services as ongoing provision.
Organization Design and Management The planning process includes the following steps: • Identify key strategic issues facing the organization • Establish overall business goals and objectives • Select strategies to address goals • Define specific objectives to each strategy. • Create measurement metrics and data sets for defining baselines and progress. • Identify key progress measures used to formally track progress.
Organization Design and Management Hoshin Planning relies on a participative base that is followed by a publicizing of the progress and as such depends on a open culture and a lack of fear.
Organization Design and Management Learning Organization • Organizations that are skilled at gaining insight from their own experiences and experience of others and modify the way they function based on this knowledge. • They used this knowledge to continuously improve the quality of care and performance related to both strategy and operations.
Organization Design and Management The orientation of the learning system: • Knowledge Source: • Internal: past internal organizational experiences • External: benchmarking • Product-Process Focus • Focus on both process and outcomes to fully understand quality and to move quality forward. • Documentation Mode • Documentation of information in the organization that is transparent and publicly available vs only available to affected individuals and group alone. • Dissemination Mode • Refers to different mode of dissemination of information and knowledge. • Consist of both formal and informal methods of interaction