Physics and the Quantum Model
120 likes | 322 Vues
Physics and the Quantum Model. Light. The idea for the the quantum mechanical model grew out of the study of light Light consists of waves The amplitude of a a wave is the height from zero to crest Wavelength ( λ ) is the distance between crests

Physics and the Quantum Model
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Light • The idea for the the quantum mechanical model grew out of the study of light • Light consists of waves • The amplitude of a a wave is the height from zero to crest • Wavelength (λ) is the distance between crests • Frequency (ν) is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time • Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz)
Light • c= λν • c is a constant, equal to 2.998 x 108 m/s, so frequency and wavelength are inversly proportional
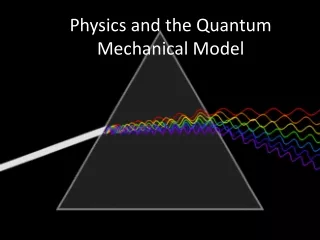
Atomic Spectra • Atoms can absorb energy that raises electrons into higher energy levels. • The electrons then lose the energy by emitting light when electrons return to their lower energy level. • The light emitted by electrons only contains certain wavelengths of light. • Each frequency corresponds to a specific color • Each element emits a unique atomic emission spectrum
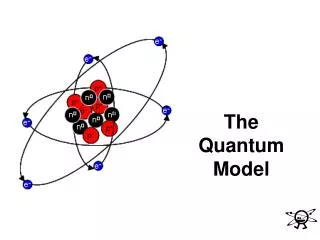
How it Works • An electron has a lowest possible energy called it’s ground state. • For hydrogen, its ground state is n=1 • Absorbing energy can excite the electron to n=2,3,4,5 or 6 • A quantum of energy in the form of light is emitted when an electron drops back to a lower energy level • The light emitted by an electron transition from higher to lower is derectly proportional to the energy change in the electron, therefore each transition produces a line of a specific frequency in the spectrum
Quantum Mechanics • Light has a dual wave/particle nature • Particles of light are called photons • Experiments showed that electrons also behaved like particles and waves • This wave like nature is used in electron microscopes since electrons have a much smaller wavelength than visible light • Quantum mechanics describes the motion of subatomic particles and atoms as waves
Heisenburg Uncertainty Principle • It is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time
Tying it Together • The discovery of matter waves paved the way for Schrodinger’s quantum mechanical atom model. His theories include the wavelike motion of matter and the uncertainty principle.