Scientific Method
50 likes | 177 Vues
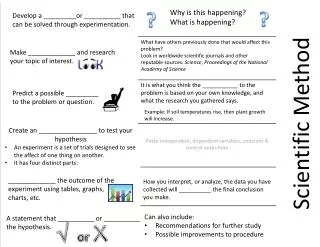
The Scientific Method is a logical, systematic approach to solving problems and understanding the world. It involves several key steps: observation to gather information, forming a hypothesis as an educated guess, testing that hypothesis through experimentation, and ultimately developing theories or laws based on the results. The method emphasizes the roles of independent and dependent variables, constants, control groups, and experimental groups. While theories provide well-tested explanations, laws summarize proven relationships and behaviors observed in nature, such as the Law of Conservation of Mass.

Scientific Method
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Scientific Method • Logical, systematic approach to solve a problem • Steps to Sci. Method: • Observe • Hypothesis • Test Hypothesis • Develop Theories/Law Scientific Method
Observation • Uses senses obtain info • Hypothesis • Educated guess • Experiment • Procedure that is used to test hypothesis Scientific Method
Variable • Factor being tested • Independent variable • What is directly changed • The “If” part of an “If…then” statement • Always think…it is what Ichanged • Hint: Try to find I.V. 1st & then the others • Dependent variable • What is indirectly changed • The “then” part of an “If…then” statement • Constant • Remains the same throughout the entire exp. • Control Group • What happens under normal conditions • To ID – look for the groups resulting from I.V. and choose 1 • Experimental Group • What happens when 1 variable is changed Parts of and Experiment
Theory • Well-tested explanation (gives the why) • NEVER proven • i.e. Big Bang Theory • Law • Summary of results (gives the what) • PROVEN • Mathematical relationship • If one increases the temp., the volume of the container increases • i.e. Law of Conservation of Mass – Matter can neither be created nor destroyed. Theory/Law