Understanding the Rock Cycle and Relationships Among Major Rock Groups
170 likes | 284 Vues
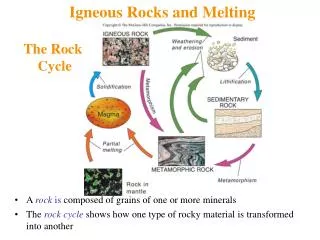
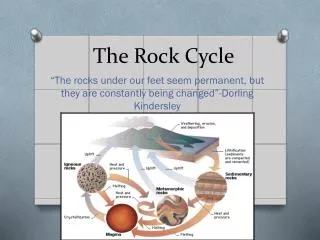
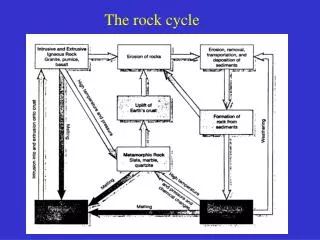
The rock cycle illustrates the dynamic relationships among the three main rock groups: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form from molten material, with plutonic (intrusive) types cooling slowly in the Earth’s crust and volcanic (extrusive) types cooling rapidly at the surface. Sedimentary rocks arise from surface processes such as erosion, transport, and deposition, encompassing clastic, chemical, and organic varieties. Metamorphic rocks undergo transformation through pressure and temperature changes. This cycle is driven by internal Earth heat, solar energy, and connects surface and interior processes.

Understanding the Rock Cycle and Relationships Among Major Rock Groups
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Rock Cycle Relationships among the major rock groups
Major Rock Groups • Igneous • Formed from molten rock • Plutonic (intrusive):slow cooling and crystallization deep w/in Earth’s crust • Volcanic (extrusion): quick cooling at the surface • Sedimentary • Formed at the Earth’s surface • Clastic (Mineral Fragments or grains, clays) • Chemical (crystalline chemical/biochemical precipitate • Organic (remains of past organisms, typically shell-bearing) • Metamorphic • Changed by pressure, temperature and fluids. • Foliated visible bands • Nonfoliated no banding pattern
Fig. 2.9 MAGMA
IGNEOUS Crystallization MAGMA
IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization MAGMA
Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization MAGMA
Weathering Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
SEDIMENT SEDIMENT Weathering Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Crystallization Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Increased Pressure & Temp METAMORPHIC Crystallization Burial Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic Can you see any shortcuts? SEDIMENTARY Increased Pressure & Temp METAMORPHIC Crystallization Melting Burial Uplift MAGMA
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Increased P&T METAMORPHIC Crystallization Melting Burial Uplift MAGMA
In Conclusion… • The rock cycle demonstrates the relationships among the three major rock groups • It is powered by the interior heat of the Earth • As well as earth’s momentum and… • The energy from the sun • It involves processes on the Earth’s surface as well as the Earth’s interior • It connects the “hydrologic cycle” with the “tectonic cycle”.
Erosion SEDIMENT Weathering Transport Deposition Volcanic IGNEOUS Plutonic SEDIMENTARY Increased P&T METAMORPHIC Crystallization Melting Burial Uplift MAGMA