SCABIES
2.1k likes | 7.05k Vues
SCABIES. Pelin özkan. Human scabies is a highly contagious disease caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis . Scabies is not primarily a sexually transmitted disease but sexual transmission does occur.

SCABIES
E N D
Presentation Transcript
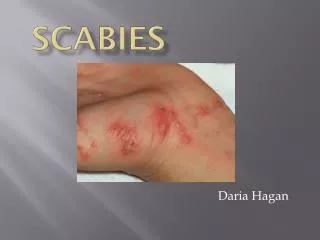
SCABIES Pelin özkan
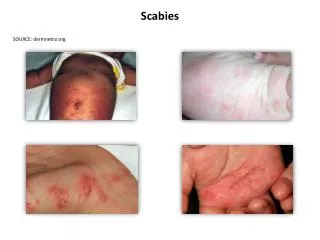
Human scabies is a highly contagious disease caused by the mite Sarcoptesscabiei var. hominis. • Scabies is not primarily a sexually transmitted disease but sexual transmission does occur. • Scabies spreads in households and neighborhoods in which there is a high frequency of intimate personal contact or sharing of inanimate objects, and fomite transmission is a major factor in household and nosocomial passage of scabies.
Immunology • A hypersensitivity reaction rather than a foreign-body response may be responsible for the lesions, which may delay recognition of symptoms of scabies.
Symptoms are minor at first and are attributed to a bite or dry skin. • Scratching destroys burrows and removes mites, providing initial relief. • The patient remains comfortable during the day but itches at night. • Primary lesions are soon destroyed by scratching.
PrimaryLesions • Mites are found in burrows and at the edge of vesicles but rarely in papules. • Burrow The linear, curved, or S-shaped burrows are approximately as wide as #2 suture material and are 2 to 15 mm long Vesicles and Papules. Vesicles are isolated and pinpoint and filled with serous rather than purulent fluid.
SecondaryLesions • Secondary lesions result from infection or are caused by scratching. • They often dominate the clinical picture. • Pinpoint erosions are the most common secondary lesions
Signs and Symptoms of Scabies • • Nodules on the penis and scrotum • • Sudden worsening of a rash present for 4 to 8 weeks • • Pustules on the palms and soles of infants • • Nocturnal itching • • Generalized, severe itching • • Pinpoint erosions and crusts on the buttocks
Signs and Symptoms of Scabies • • Vesicles in the finger webs • • Diffuse eruption sparing the face • • Patient improves and then worsens after treatment with topical steroids • • Rash present in several members of the same family • • Patient (especially an infant) develops more extensive rash despite treatment with antibiotics and topical medications
Diagnosis Dermoscopy
Treatmentand Management • Permethrin (Elimitecream) • Lindane • BenzylBenzoate • Crotamiton (EuraxLotion) • Sulfur, • Ivermectin (Stromectol)