Transcription vs Translation
120 likes | 394 Vues
Transcription vs Translation. Central Dogma. Translation. Transcription. Chargaff’s Rule. States that base ratio is 1:1 A=T CΞG Therefore if there are 300 Adenines there should also be 300 Thymines in DNA. Transcription .

Transcription vs Translation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
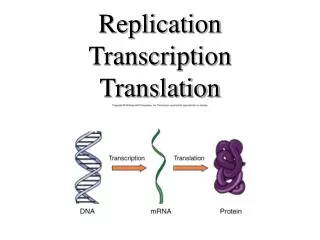
Central Dogma Translation Transcription
Chargaff’s Rule • States that base ratio is 1:1 • A=T • CΞG • Therefore if there are 300 Adenines there should also be 300 Thymines in DNA
Transcription • Initiation – RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region on the DNA and begins to unzip the DNA. Promoter normally contains TATA box, sequence of T-A-T-A
Transcription • Elongation occurs as RNA polymerase unzips the DNA and assembles RNA nucleotides using one strand of the DNA as a template. • This occurs in the 5’ 3’ direction
Transcription • Termination occurs when the RNA polymerase reaches a special sequence of nucleotides that servers as a termination point. In eukaryotes the termination region is often AAAAAAAAAAA.
mRNA processing • Before mRNA can leave the nucleus several things happen: • 5’ cap is added, cap is guanine nucleotide with 2 extra phosphates • Poly A tail added to 3’ end. Tail has about 200 adenine nucleotides. • RNA splicing – introns are removed, exons are spliced together. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins or snRNP’s delete the introns • Alternative splicing
RNA splicing Appropriately joined Protein Introns Exons
Translation • Initiation begins when the small ribosomal subunit attaches near the 5’ end of mRNA • A tRNA carrying an amino acid attaches to the mRNA at the start codon AUG. • The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the mRNA forming a complete ribosome • Elongation begins when the next tRNA binds Translation