Innovative Robot Design Project Summary - RIT Embassy Program
170 likes | 287 Vues
This project, sponsored by EME Dept., ARM, Harris, Dr. Mondragon, Cypress, RIM Team, aims to showcase the creativity and skills of RIT students. Over 4 years, the project focused on redesigning existing systems, reducing the learning curve for future groups, and enabling quicker problem-solving processes. The concept involved redesigning voltage regulators, simplifying debugging, enhancing sensor functionality, and implementing a quick disconnect system. The communication interface design utilized a remote control running as a website on the client, with AJAX requests managing robot control and sensor data updates. System testing results showed successful sonar and infrared sensor testing, although some final integrations were pending. The project achieved successes like improved robot movement, voltage regulator redesign, PCB cleanup, live video streaming, and a second-place win in the ARM design competition. Future work includes expanding autonomous capabilities, adding GPS functionality, and potential PSoC and compass integrations. With a final budget of $1220 and generous donations, the project demonstrated innovation and collaborative effort among students and sponsors.

Innovative Robot Design Project Summary - RIT Embassy Program
E N D
Presentation Transcript
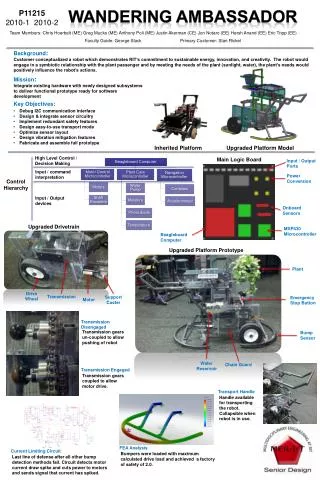
Wandering Ambassador P12215 Sponsors: EME Dept., ARM, Harris, Dr. Mondragon, Cypress, RIM
Project Statement • 4 years of project legacy • Showcase creativity and aptitude of RIT students • Reduce learning curve for future groups • Enable quicker problem solving • Parallel multidisciplinary development
Customer Needs • Redesign and Simplification of Existing Systems without Loss of Performance • Reduce Learning Curve for Future Groups • Create Test Environment and Implement a Quick Disconnect System
Concept Summary Initial Problems • Over heating voltage regulators • Large learning curve • Very difficult to debug • Sensors not functioning properly • Crowded workspace • “Rats nest” of wires • Difficult programing architecture • Too much going on
Concept Summary Current Standings • Voltage regulator redesign with heat sinks • Simple debugging Protocol • Working sensors which report values • Disconnect system integrated • PCB Redesign • Tips and Tricks for next group • Stripped of unnecessary sensors
Communication Interface Design • The remote control • Interface runs as a website on the client, in a browser • When push buttons are pressed to control robot, AJAX request is sent to Pandaboard. AJAX requests to get and update sensor values are sent in timed intervals automatically. • Pandaboard • Python Webserver reads the incoming requests/commands and processes them • If it’s a low level command (move command or sensor read command), request is forwarded to cypress and if there is any response, it is sent back to the client • If it’s a high level command (Auto navigate or servo scan mode), it launches threads that automate sending of low level commands • If its halt command, threads are stopped and halt is also issued to cypress • Cypress • Continuously monitors its UART ports for commands • When a command is received, it interprets the command, calls the necessary function and returns a value if necessary
System Testing Results-Sonar Sonar testing was done by centering the robot sonar along a seam in the tiles on the floor. Markers were then laid out every foot, with 0 being on the ground directly underneath the sonar. A large flat object was then placed in front of the sonar at every foot interval. The sonar returns an analog voltage that when used in conjunction with a scaling factor, determines the sensed distance. To test the beam width, at the distances shown below, the same object was placed in the center, then moved off to the side incrementally until the sonar did not detect it. Interestingly there are some fringe effects right on the cusp of the beam. More measurements were not taken for beam width because of the relatively slow rate of increase.
System Testing Results-Infrared The infrared sensors were tested the same was as the sonars. The distance cannot be obtained as easily as it was for the sonars, however. Measurements have to be taken and a line-fit (shown below) has to be applied to find the function to determine the sensed distance.
Not Fully Functional •Integration of IR sensors into auto-navigation •Compass modulation testing/incorporation into final design •GPS location of robot had not been integrated into design • Exceeded budget by $320 Objective Project Evaluation Successes •Proper robot forward, reverse, left and right movement •Quick disconnect system to enable use of mule for testing purposes •Redesign of voltage regulators •Significant cleanup and organization of PCB board •Live video stream through website •Tricks/tips manuals to help future teams quickly learn current design •Current project design allows for future teams to develop without need for total redesign of PCB •Robot has been developed such that high level auto navigation can be implemented with the proper programming •Inclusion of prototype area for future developmental purposes •Diagnostic GUI, which can be displayed on computer using website • Won Second Place in the ARM design competition
Future Work • Room for expansion • Further autonomous capabilities • A second PSoC can be added to prototype area • GPS capabilities • Compass
Expenses & Donations • Final budget spent ~$1220 • Donated items: • Pandaboard ($180) • Cypress PSoC 3/5 ($50) • Sparkfun RS232 Level Shifter ($20) • Blackberry PlayBook ($200) *Donated by Dr. Mondragon